A Comparative Study on Functional Recovery, Complications, and Changes in Inflammatory Factors in Patients with Thoracolumbar Spinal Fracture Complicated with Nerve Injury Treated by Anterior and Posterior Decompression
- PMID: 30753178
- PMCID: PMC6380160
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.912332
A Comparative Study on Functional Recovery, Complications, and Changes in Inflammatory Factors in Patients with Thoracolumbar Spinal Fracture Complicated with Nerve Injury Treated by Anterior and Posterior Decompression
Abstract
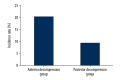
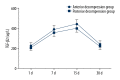
BACKGROUND The aim of this study was to evaluate 2 methods to treat patients with thoracic lumbar spine fracture with merging spinal cord injury, including complications of surgery and the influence of inflammatory factors. MATERIAL AND METHODS Eighty patients were randomly divided into an anterior decompression group (study group) or a posterior decompression group (control group) to observe perioperative complications, evaluate preoperative and postoperative nerve function, and evaluate the 6-month injured vertebral height and Cobb angle of the vertebral bodies. The expression level of TGF-β₂ on day 1, day 7, day 15, and day 30 after treatment was detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). RESULTS The nerve function sensation score, the height of the vertebral body, and the recovery of Cobb angle were better for the anterior decompression group than the posterior decompression group and the effect was significant (P<0.05). The complication rate for the posterior decompression group was lower than the anterior decompression group. The level of TGF-β₂ in the anterior decompression group was higher than in the posterior decompression group for the same times: after day 1, day 7, day 15, and day 30 after treatment (P<0.05). CONCLUSIONS Patients who had thoracic lumbar spine fracture with merging spinal cord injury and who had anterior fixation achieved a good fixation effect; their neurologic and vertebral injury recovery was better. However, this relatively complex and traumatic surgery must consider the clinical manifestations and fractures of the patients and select the appropriate surgical approach.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by posterior laminotomy decompression and bone grafting via injured vertebrae].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014 Oct;28(10):1236-40. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25591299 Chinese.
-
[Posterior spinal canal decompression with screw fixation and reconstruction of three vertebral column for thoracolumbar burst fractures complicated with nerve injury].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2018 Apr 25;31(4):322-327. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0034.2018.04.006. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2018. PMID: 29772857 Chinese.
-
[Curative effect of anterolateral spinal canal decompression combined with short segment screw fixation with posterior approach for severe thoracolumbar burst fractures with spinal cord injury].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2020 Dec 25;33(12):1128-33. doi: 10.12200/j.issn.1003-0034.2020.12.009. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2020. PMID: 33369320 Chinese.
-
Combined anterior and posterior surgery for fractures of the thoracolumbar spine.Instr Course Lect. 1999;48:443-9. Instr Course Lect. 1999. PMID: 10098075 Review. No abstract available.
-
Posterior Pedicle Screw Fixation With Indirect Decompression Versus Direct Decompression in Treating Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.World Neurosurg. 2024 Jun;186:27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2024.03.040. Epub 2024 Mar 15. World Neurosurg. 2024. PMID: 38493890
Cited by
-
Unilateral biportal endoscopic decompression combined with percutaneous pedicle screw fixation offers new treatment option for thoracolumbar burst fractures with secondary spinal stenosis.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 6;15(1):877. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-85543-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39762475 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of anterior versus posterior approach for the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Mar;10(6):309. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-903. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35433975 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical management of thoracolumbar junction fractures: An evidence-based algorithm.World Neurosurg X. 2023 Jan 20;17:100151. doi: 10.1016/j.wnsx.2022.100151. eCollection 2023 Jan. World Neurosurg X. 2023. PMID: 36793355 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Anterior and Posterior Decompressions in Treatment of Traumatic Thoracolumbar Spinal Fractures Complicated with Spinal Cord Injury.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Nov 19;26:e927284. doi: 10.12659/MSM.927284. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 33211674 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Analysis of the Relationship Between Modic Change and Spinopelvic Parameters in the Sagittal Plane.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Jan 29;26:e919667. doi: 10.12659/MSM.919667. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 31994493 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wand F, Zhu Y. Treatment of complete fracture-dislocation of thoracolumbar spine. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(8):421–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical