Frequency-resolved analysis of coherent oscillations of local cerebral blood volume, measured with near-infrared spectroscopy, and systemic arterial pressure in healthy human subjects
- PMID: 30753203
- PMCID: PMC6372153
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0211710
Frequency-resolved analysis of coherent oscillations of local cerebral blood volume, measured with near-infrared spectroscopy, and systemic arterial pressure in healthy human subjects
Abstract
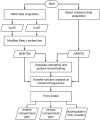
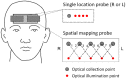
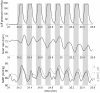
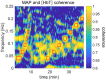
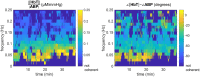
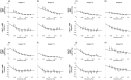
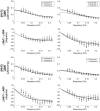
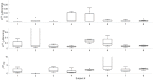
We report a study on twenty-two healthy human subjects of the dynamic relationship between cerebral hemoglobin concentration ([HbT]), measured with near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) in the prefrontal cortex, and systemic arterial blood pressure (ABP), measured with finger plethysmography. [HbT] is a measure of local cerebral blood volume (CBV). We induced hemodynamic oscillations at discrete frequencies in the range 0.04-0.20 Hz with cyclic inflation and deflation of pneumatic cuffs wrapped around the subject's thighs. We modeled the transfer function of ABP and [HbT] in terms of effective arterial (K(a)) and venous (K(v)) compliances, and a cerebral autoregulation time constant (τ(AR)). The mean values (± standard errors) of these parameters across the twenty-two subjects were K(a) = 0.01 ± 0.01 μM/mmHg, K(v) = 0.09 ± 0.05 μM/mmHg, and τ(AR) = 2.2 ± 1.3 s. Spatially resolved measurements in a subset of eight subjects reveal a spatial variability of these parameters that may exceed the inter-subject variability at a set location. This study sheds some light onto the role that ABP and cerebral blood flow (CBF) play in the dynamics of [HbT] measured with NIRS, and paves the way for new non-invasive optical studies of cerebral blood flow and cerebral autoregulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Czosnyka M, Hutchinson PJ, Balestreri M, Hiller M, Smielewski P, Pickard JD. Monitoring and interpretation of intracranial pressure after head injury. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2006;96(114–8). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

