Adalimumab Effectiveness Up to Six Years in Adalimumab-naïve Patients with Crohn's Disease: Results of the PYRAMID Registry
- PMID: 30753510
- PMCID: PMC6701510
- DOI: 10.1093/ibd/izz008
Adalimumab Effectiveness Up to Six Years in Adalimumab-naïve Patients with Crohn's Disease: Results of the PYRAMID Registry
Abstract
Background: PYRAMID was an international multicenter, noninterventional, postmarketing registry assessing long-term safety and effectiveness of adalimumab (Humira), as used in routine clinical practice.
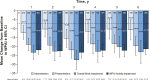
Methods: Adult patients with moderately to severely active Crohn's disease with or without prior adalimumab experience were enrolled in the registry and followed for up to 6 years. Effectiveness measurements included the Physician's Global Assessment (PGA, a composite of Harvey Bradshaw Index [HBI] and rectal bleeding score), clinical remission (HBI < 5), Short Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire (SIBDQ), and Work Productivity and Activity Impairment (WPAI) questionnaire. Data were reported for adalimumab-naïve patients and analyzed by baseline immunomodulator use and disease duration.
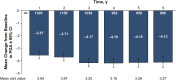
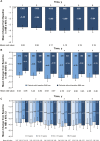
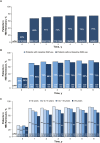
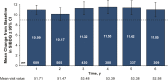
Results: This study evaluated 2057 adalimumab-naïve patients. Mean PGA improved from 7.5 (baseline) to 3.9 (year 1) and 3.3 (year 6). The proportion of patients in HBI remission increased from 29% (573 of 1969; baseline) to 68% (900 of 1331; year 1) and 75% (625 of 831; year 6). Patients stratified by baseline immunomodulator use had similar HBI remission rates; patients with disease duration <2 years achieved numerically higher HBI remission rates than patients with longer disease duration. Patient-reported SIBDQ and WPAI scores improved at year 1; all WPAI subscore improvements were clinically meaningful (≥7% point change) at year 1 and maintained through year 6. Serious infections were reported in 11.1% of patients; incidence rates of malignancies, lymphoma, and demyelinating disorders were low.
Conclusion: Adalimumab therapy, as used in routine clinical practice, improved physician-reported and patient-reported disease outcomes and remission rates for up to 6 years. No new safety signals were observed.
Keywords: clinical practice; disease activity; long-term effectiveness; long-term safety; work productivity.
© 2019 Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of adalimumab in Canadian patients with moderate to severe Crohn's disease: results of the Adalimumab in Canadian SubjeCts with ModErate to Severe Crohn's DiseaSe (ACCESS) trial.Can J Gastroenterol. 2011 Aug;25(8):419-25. doi: 10.1155/2011/724813. Can J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21912766 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Adalimumab by Disease Duration: Analysis of Pooled Data From Crohn's Disease Studies.J Crohns Colitis. 2019 May 27;13(6):725-734. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjy223. J Crohns Colitis. 2019. PMID: 30753371 Free PMC article.
-
Adalimumab produces clinical remission and reduces extraintestinal manifestations in Crohn's disease: results from CARE.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2012 Jan;18(1):1-9. doi: 10.1002/ibd.21663. Epub 2011 Feb 23. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2012. PMID: 21351211 Clinical Trial.
-
[Anti-TNF therapy in treatment of luminal Crohn's disease].Acta Med Croatica. 2013 Apr;67(2):179-89. Acta Med Croatica. 2013. PMID: 24471301 Review. Croatian.
-
A comprehensive review and update on Crohn's disease.Dis Mon. 2018 Feb;64(2):20-57. doi: 10.1016/j.disamonth.2017.07.001. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Dis Mon. 2018. PMID: 28826742 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Originator Infliximab Treatment on Disease-Related Hospitalizations, Work Productivity and Activity Impairment, and Health Resource Utilization in Patients with Crohn's Disease in a Real-Life Setting: Results of a Prospective Multicenter Study in Germany.Inflamm Intest Dis. 2021 Feb;6(1):48-60. doi: 10.1159/000512159. Epub 2020 Dec 18. Inflamm Intest Dis. 2021. PMID: 33850839 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of adalimumab effects on left ventricle performance by echocardiography indexes among patients with immunosuppressant refractory ulcerative colitis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 6;9:1008711. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1008711. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36687438 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy, Safety, and Immunogenicity of SDZ-ADL, an Adalimumab Biosimilar, in Biologic-Naïve and Switched Patients with Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases: A Literature Review.Adv Ther. 2025 Mar;42(3):1360-1392. doi: 10.1007/s12325-024-03098-z. Epub 2025 Feb 5. Adv Ther. 2025. PMID: 39907897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incidence comparison of adverse events in patients with inflammatory bowel disease receiving different biologic agents: retrospective long-term evaluation.Intest Res. 2022 Jan;20(1):114-123. doi: 10.5217/ir.2021.00037. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Intest Res. 2022. PMID: 34333908 Free PMC article.
-
Work Productivity Impairment in Persons with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Crohns Colitis. 2024 Sep 3;18(9):1486-1504. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjae057. J Crohns Colitis. 2024. PMID: 38647194 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lichtiger S, Binion DG, Wolf DC, et al. . The CHOICE trial: adalimumab demonstrates safety, fistula healing, improved quality of life and increased work productivity in patients with Crohn’s disease who failed prior infliximab therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010;32:1228–1239. - PubMed
-
- Longobardi T, Jacobs P, Bernstein CN. Work losses related to inflammatory bowel disease in the United States: results from the National Health Interview Survey. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:1064–1072. - PubMed
-
- Colombel JF, Rutgeerts PJ, Sandborn WJ, et al. . Adalimumab induces deep remission in patients with Crohn’s disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;12:414–422.e415. - PubMed
-
- Colombel JF, Sandborn WJ, Panaccione R, et al. . Adalimumab safety in global clinical trials of patients with Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009;15:1308–1319. - PubMed
-
- Colombel JF, Sandborn WJ, Rutgeerts P, et al. . Adalimumab for maintenance of clinical response and remission in patients with Crohn’s disease: the CHARM trial. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:52–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

