Validation of the nearest-neighbor model for Watson-Crick self-complementary DNA duplexes in molecular crowding condition
- PMID: 30753582
- PMCID: PMC6468326
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkz071
Validation of the nearest-neighbor model for Watson-Crick self-complementary DNA duplexes in molecular crowding condition
Abstract
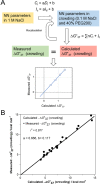
Recent advancement in nucleic acid techniques inside cells demands the knowledge of the stability of nucleic acid structures in molecular crowding. The nearest-neighbor model has been successfully used to predict thermodynamic parameters for the formation of nucleic acid duplexes, with significant accuracy in a dilute solution. However, knowledge about the applicability of the model in molecular crowding is still limited. To determine and predict the stabilities of DNA duplexes in a cell-like crowded environment, we systematically investigated the validity of the nearest-neighbor model for Watson-Crick self-complementary DNA duplexes in molecular crowding. The thermodynamic parameters for the duplex formation were measured in the presence of 40 wt% poly(ethylene glycol)200 for different self-complementary DNA oligonucleotides consisting of identical nearest-neighbors in a physiological buffer containing 0.1 M NaCl. The thermodynamic parameters as well as the melting temperatures (Tm) obtained from the UV melting studies revealed similar values for the oligonucleotides having identical nearest-neighbors, suggesting the validity of the nearest-neighbor model in the crowding condition. Linear relationships between the measured ΔG°37 and Tm in crowding condition and those predicted in dilute solutions allowed us to predict ΔG°37, Tm and nearest-neighbor parameters in molecular crowding using existing parameters in the dilute condition, which provides useful information about the thermostability of the self-complementary DNA duplexes in molecular crowding.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures



References
-
- Saiki R.K., Gelfand D.H., Stoffel S., Scharf S.J., Higuchi R., Horn G.T., Mullis K.B., Erlich H.A.. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988; 239:487–491. - PubMed
-
- Fodor S.P., Rava R.P., Huang X.C., Pease A.C., Holmes C.P., Adams C.L.. Multiplexed biochemical assays with biological chips. Nature. 1993; 364:555–556. - PubMed
-
- Crooke S.T., Lebleu B.. Antisense Research and Applications. 1993; Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

