Environmental enteric dysfunction and child stunting
- PMID: 30753710
- PMCID: PMC6394759
- DOI: 10.1093/nutrit/nuy068
Environmental enteric dysfunction and child stunting
Abstract
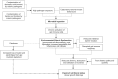
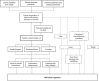
In 2017, an estimated 1 in every 4 (23%) children aged < 5 years were stunted worldwide. With slow progress in stunting reduction in many regions and the realization that a large proportion of stunting is not due to insufficient diet or diarrhea alone, it remains that other factors must explain continued growth faltering. Environmental enteric dysfunction (EED), a subclinical state of intestinal inflammation, can occur in infants across the developing world and is proposed as an immediate causal factor connecting poor sanitation and stunting. A result of chronic pathogen exposure, EED presents multiple causal pathways, and as such the scope and sensitivity of traditional water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) interventions have possibly been unsubstantial. Although the definite pathogenesis of EED and the mechanism by which stunting occurs are yet to be defined, this paper reviews the existing literature surrounding the proposed pathology and transmission of EED in infants and considerations for nutrition and WASH interventions to improve linear growth worldwide.
Keywords: WASH; early child development; environmental enteric dysfunction; malnutrition; sanitation; stunting.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the International Life Sciences Institute.
Figures
References
-
- United Nations’ Children’s Fund, World Health Organization, World Bank. Joint Child Malnutrition Estimates—Levels and Trends. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, 2017. Available at: http://www.who.int/nutgrowthdb/estimates2016/en/. Accessed December 15, 2017.
-
- WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study Group . WHO Child Growth Standards: Length/Height-for-Age, Weight-for-Age, Weight-for-Length, Weight-for-Height and Body Mass Index-for-Age: Methods and Development. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, 2006.
-
- United Nations’ Children’s Fund. Malnutrition: current status and progress. 2017. Available at: https://data.unicef.org/topic/nutrition/malnutrition/#. Accessed December 15, 2017.
-
- Black R, Victora C, Walker S, et al. Maternal and child undernutrition and overweight in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet. 2013;382:427–451. - PubMed

