Effect of plasma MicroRNA on antihypertensive response to beta blockers in the Pharmacogenomic Evaluation of Antihypertensive Responses (PEAR) studies
- PMID: 30753892
- PMCID: PMC6467266
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejps.2019.02.013
Effect of plasma MicroRNA on antihypertensive response to beta blockers in the Pharmacogenomic Evaluation of Antihypertensive Responses (PEAR) studies
Abstract
β-blockers show variable efficacy as antihypertensives. Herein, we evaluated plasma miRNAs as biomarkers for defining antihypertensive response to β-blockers. Expression of 22 β-blocker pharmacodynamics-related miRNAs was assessed in baseline plasma samples from 30 responders and 30 non-responders to metoprolol from the PEAR-2 study (Discovery). Logistic regression was performed to identify miRNAs significantly associated with metoprolol response. Those miRNAs were profiled in baseline plasma samples from 25 responders and 25 non-responders to atenolol from the PEAR study (validation). In discovery, miR-101, miR-27a, miR-22, miR-19a, and let-7e were significantly associated with metoprolol response (P = 0.01, 0.017, 0.025, 0.025, and 0.04, respectively). In validation, miR-19a was significantly associated with atenolol response (P = 0.038). Meta-analysis between PEAR-2 and PEAR revealed significant association between miR-19a (P = 0.004), miR-101 (P = 0.006), and let-7e (P = 0.012) and β-blocker response. Hence, miR-19a, miR-101, and let-7e, which regulate β1-adrenergic receptor and other β-blocker pharmacodynamics-related genes, may be biomarkers for antihypertensive response to β-blockers.
Keywords: Antihypertensive response; Beta-blocker; Biomarker; Hypertension; microRNA.
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures

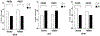
Similar articles
-
Genomic Association Analysis Reveals Variants Associated With Blood Pressure Response to Beta-Blockers in European Americans.Clin Transl Sci. 2019 Sep;12(5):497-504. doi: 10.1111/cts.12643. Epub 2019 Jun 4. Clin Transl Sci. 2019. PMID: 31033190 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
β-blockers: a review of their pharmacological and physiological diversity in hypertension.Ann Pharmacother. 2014 Jun;48(6):723-33. doi: 10.1177/1060028013519591. Epub 2014 Mar 31. Ann Pharmacother. 2014. PMID: 24687542 Review.
-
Beta-blocker subtypes and risk of low birth weight in newborns.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2018 Nov;20(11):1603-1609. doi: 10.1111/jch.13397. Epub 2018 Sep 28. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2018. PMID: 30267456 Free PMC article.
-
β2 -Adrenergic Receptor Gene Affects the Heart Rate Response of β-Blockers: Evidence From 3 Clinical Studies.J Clin Pharmacol. 2019 Nov;59(11):1462-1470. doi: 10.1002/jcph.1443. Epub 2019 May 14. J Clin Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31090079 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Beta-adrenergic antagonists in hypertension: a review of the evidence.Ann Pharmacother. 2009 Dec;43(12):2031-43. doi: 10.1345/aph.1M381. Ann Pharmacother. 2009. PMID: 19934392 Review.
Cited by
-
A Machine Learning Model Based on microRNAs for the Diagnosis of Essential Hypertension.Noncoding RNA. 2023 Oct 25;9(6):64. doi: 10.3390/ncrna9060064. Noncoding RNA. 2023. PMID: 37987360 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating MicroRNA as Biomarkers of Anthracycline-Induced Cardiotoxicity: JACC: CardioOncology State-of-the-Art Review.JACC CardioOncol. 2024 Feb 27;6(2):183-199. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2023.12.009. eCollection 2024 Apr. JACC CardioOncol. 2024. PMID: 38774014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypertension precision medicine: the promise and pitfalls of pharmacogenomics.Pharmacogenomics. 2025 Apr-Apr;26(5-6):183-206. doi: 10.1080/14622416.2025.2504865. Epub 2025 May 27. Pharmacogenomics. 2025. PMID: 40421951 Review.
-
Circulating microRNA Related to Cardiometabolic Risk Factors for Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review.Metabolites. 2022 Oct 30;12(11):1044. doi: 10.3390/metabo12111044. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36355127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peripheral blood microRNAs and the COVID-19 patient: methodological considerations, technical challenges and practice points.RNA Biol. 2021 May;18(5):688-695. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2021.1885188. Epub 2021 Feb 15. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 33530819 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen X, et al., 2008. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 18, 997–1006. - PubMed
-
- Chen Q, et al., 2013. Serum miR-19a predicts resistance to FOLFOX chemotherapy in advanced colorectal cancer cases. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev 14, 7421–7426. - PubMed
-
- Egan BM, et al., 2010. US trends in prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension, 1988–2008. JAMA 303, 2043–2050. - PubMed
-
- Farh KK, et al., 2005. The widespread impact of mammalian MicroRNAs on mRNA repression and evolution. Science 310, 1817–1821. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

