C/EBPβ Is a Transcriptional Regulator of Wee1 at the G₂/M Phase of the Cell Cycle
- PMID: 30754676
- PMCID: PMC6407104
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8020145
C/EBPβ Is a Transcriptional Regulator of Wee1 at the G₂/M Phase of the Cell Cycle
Abstract
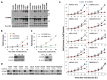
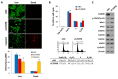
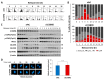
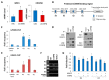
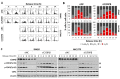
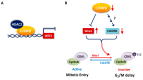
The CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β (C/EBPβ) is a transcription factor that regulates cellular proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis and tumorigenesis. Although the pro-oncogenic roles of C/EBPβ have been implicated in various human cancers, how it contributes to tumorigenesis or tumor progression has not been determined. Immunohistochemistry with human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tissues revealed that higher levels of C/EBPβ protein were expressed compared to normal lung tissues. Knockdown of C/EBPβ by siRNA reduced the proliferative capacity of NSCLC cells by delaying the G₂/M transition in the cell cycle. In C/EBPβ-knockdown cells, a prolonged increase in phosphorylation of cyclin dependent kinase 1 at tyrosine 15 (Y15-pCDK1) was displayed with simultaneously increased Wee1 and decreased Cdc25B expression. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis showed that C/EBPβ bound to distal promoter regions of WEE1 and repressed WEE1 transcription through its interaction with histone deacetylase 2. Treatment of C/EBPβ-knockdown cells with a Wee1 inhibitor induced a decrease in Y15-pCDK1 and recovered cells from G₂/M arrest. In the xenograft tumors, the depletion of C/EBPβ significantly reduced tumor growth. Taken together, these results indicate that Wee1 is a novel transcription target of C/EBPβ that is required for the G₂/M phase of cell cycle progression, ultimately regulating proliferation of NSCLC cells.
Keywords: C/EBPβ; G2/M arrest; Wee1; Y15-pCDK1; cell cycle; lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Quantitative Phosphoproteomics Reveals Wee1 Kinase as a Therapeutic Target in a Model of Proneural Glioblastoma.Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 Jun;15(6):1332-43. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0692. Epub 2016 May 17. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 27196784 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of targeting the FLNA-regulated Wee1 kinase in adrenocortical carcinomas.Int J Cancer. 2025 Mar 15;156(6):1256-1271. doi: 10.1002/ijc.35239. Epub 2024 Nov 11. Int J Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39528354 Free PMC article.
-
Disulfiram/copper complex improves the effectiveness of the WEE1 inhibitor Adavosertib in p53 deficient non-small cell lung cancer via ferroptosis.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2024 Dec;1870(8):167455. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2024.167455. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2024. PMID: 39111630
-
WEE1 tyrosine kinase, a novel epigenetic modifier.Trends Genet. 2013 Jul;29(7):394-402. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2013.02.003. Epub 2013 Mar 26. Trends Genet. 2013. PMID: 23537585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stop and go: anti-proliferative and mitogenic functions of the transcription factor C/EBPbeta.Cell Cycle. 2006 May;5(9):953-7. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.9.2733. Epub 2006 May 1. Cell Cycle. 2006. PMID: 16687924 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel signature predicts prognosis and immunotherapy in lung adenocarcinoma based on cancer-associated fibroblasts.Front Immunol. 2023 May 31;14:1201573. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1201573. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37325647 Free PMC article.
-
C/EBPβ Regulates HIF-1α-Driven Invasion of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells.Biomolecules. 2024 Dec 30;15(1):36. doi: 10.3390/biom15010036. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39858431 Free PMC article.
-
rs822336 binding to C/EBPβ and NFIC modulates induction of PD-L1 expression and predicts anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy in advanced NSCLC.Mol Cancer. 2024 Mar 25;23(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-01976-2. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38528526 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of lncRNA X inactive specific transcript (XIST) radiosensitizes non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells through regulation of miR-16-5p/WEE1 G2 checkpoint kinase (WEE1) axis.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2021 Jan-Dec;35:2058738420966087. doi: 10.1177/2058738420966087. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33583218 Free PMC article.
-
C/EBPβ Promotes LPS-Induced IL-1β Transcription and Secretion in Alveolar Macrophages via NOD2 Signaling.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Sep 11;15:5247-5263. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S377499. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 36120185 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

