Gli Proteins: Regulation in Development and Cancer
- PMID: 30754706
- PMCID: PMC6406693
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8020147
Gli Proteins: Regulation in Development and Cancer
Abstract
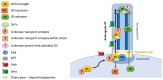
Gli proteins are transcriptional effectors of the Hedgehog signaling pathway. They play key roles in the development of many organs and tissues, and are deregulated in birth defects and cancer. We review the molecular mechanisms of Gli protein regulation in mammals, with special emphasis on posttranslational modifications and intracellular transport. We also discuss how Gli proteins interact with co-activators and co-repressors to fine-tune the expression of Hedgehog target genes. Finally, we provide an overview of the regulation of developmental processes and tissue regeneration by Gli proteins and discuss how these proteins are involved in cancer progression, both through canonical regulation via the Hedgehog pathway and through cross-talk with other signaling pathways.
Keywords: Gli proteins; Hedgehog signaling; cancer; developmental signaling; morphogen signaling; nuclear import; posttranslational modifications; primary cilia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lettice L.A., Heaney S.J.H., Purdie L.A., Li L., de Beer P., Oostra B.A., Goode D., Elgar G., Hill R.E., de Graaff E. A long-range Shh enhancer regulates expression in the developing limb and fin and is associated with preaxial polydactyly. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2003;12:1725–1735. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddg180. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources