Simultaneous Determination of Pharmaceuticals by Solid-phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry: A Case Study from Sharjah Sewage Treatment Plant
- PMID: 30754718
- PMCID: PMC6385045
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24030633
Simultaneous Determination of Pharmaceuticals by Solid-phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry: A Case Study from Sharjah Sewage Treatment Plant
Abstract
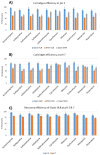
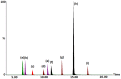
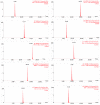
The present work describes the optimization and validation of a highly selective and sensitive analytical method using solid phase extraction and liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (SPE LC-MS/MS) for the determination of some frequently prescribed pharmaceuticals in urban wastewater received and treated by Sharjah sewage treatment plant (STP). The extraction efficiency of different SPE cartridges was tested and the simultaneous extraction of pharmaceuticals was successfully accomplished using hydrophilic-lipophilic-balanced reversed phase Waters® Oasis HLB cartridge (200 mg/ 6 mL) at pH 3. The analytes were separated on an Aquity BEH C18 column (1.7 µm, 2.1 mm × 150 mm) using gradient elution and mass spectrometric analysis were performed in multiple reactions monitoring (MRM) selecting two precursor ions to produce ion transition for each pharmaceutical using positive electrospray ionization (+ESI) mode. The correlation coefficient values in the linear calibration plot for each target compound exceeded 0.99 and the recovery percentages of the investigated pharmaceuticals were more than 84%. Limit of detection (LOD) varied between 0.1⁻1.5 ng/L and limit of quantification (LOQ) was 0.3⁻5 ng/L for all analytes. The precision of the method was calculated as the relative standard deviation (RSD%) of replicate measurements and was found to be in the ranges of 2.2% to 7.7% and 2.2% to 8.6% for inter and intra-day analysis, respectively. All of the obtained validation parameters satisfied the requirements and guidelines of analytical method validation.
Keywords: liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry; pharmaceuticals; solid phase extraction; wastewater analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Daflon S., Guerra I., Reynier M., Cerqueira A., Botta R., Campos J. Toxicity identification and evaluation (TIE) of a petroleum refinery wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. Health Tox. Hazard Subst. Environ. Eng. 2017;29:842–848. - PubMed
-
- Rivera-Jaimes J.A., Postigo C., Melgoza-Alemán R.M., Aceña J., Barceló D., López de Alda M. Study of pharmaceuticals in surface and wastewater from Cuernavaca, Morelos, Mexico: Occurrence and environmental risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018;613:1263–1274. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.134. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Siedlewicz G., Białk-Bielińska A., Borecka M., Winogradow A., Stepnowski P., Pazdro K. Presence, concentrations and risk assessment of selected antibiotic residues in sediments and near-bottom waters collected from the Polish coastal zone in the southern Baltic Sea -Summary of 3 years of studies. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018;129:787–801. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.10.075. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

