Direct, Real-Time Detection of Adenosine Triphosphate Release from Astrocytes in Three-Dimensional Culture Using an Integrated Electrochemical Aptamer-Based Sensor
- PMID: 30754968
- PMCID: PMC6469990
- DOI: 10.1021/acschemneuro.9b00033
Direct, Real-Time Detection of Adenosine Triphosphate Release from Astrocytes in Three-Dimensional Culture Using an Integrated Electrochemical Aptamer-Based Sensor
Abstract
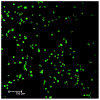
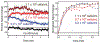
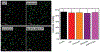
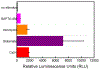
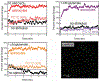
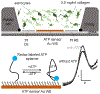
In this manuscript, we describe the development and application of electrochemical aptamer-based (E-AB) sensors directly interfaced with astrocytes in three-dimensional (3D) cell culture to monitor stimulated release of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The aptamer-based sensor couples specific detection of ATP, selective performance directly in cell culture media, and seconds time resolution using squarewave voltammetry for quantitative ATP-release measurements. More specifically, we demonstrate the ability to quantitatively monitor ATP release into the extracellular environment after stimulation by the addition of calcium (Ca2+), ionomycin, and glutamate. The sensor response is confirmed to be specific to ATP and requires the presence of astrocytes in culture. For example, PC12 cells do not elicit a sensor response after stimulation with the same stimulants. In addition, we confirmed cell viability in the collagen matrix for all conditions tested. Our hydrogel-sensor interface offers the potential to study the release of small molecule messengers in 3D environments. Given the generality of electrochemical aptamer-based sensors and the demonstrated successful interfacing of sensors with tissue scaffold material, in the long term, we anticipate our sensors will be able to translate from in vitro to in vivo small molecule recordings.
Keywords: 3D cell culture; ATP; aptamer-based sensor; astrocytes; electrochemistry; gliotransmission.
Figures
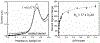
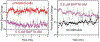
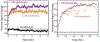
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

