Metabolite concentration changes associated with positive and negative BOLD responses in the human visual cortex: A functional MRS study at 7 Tesla
- PMID: 30755134
- PMCID: PMC7026843
- DOI: 10.1177/0271678X19831022
Metabolite concentration changes associated with positive and negative BOLD responses in the human visual cortex: A functional MRS study at 7 Tesla
Abstract
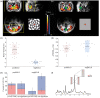
Negative blood oxygenation-level dependent (BOLD) signal observed during task execution in functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) can be caused by different mechanisms, such as a blood-stealing effect or neuronal deactivation. Electrophysiological recordings showed that neuronal deactivation underlies the negative BOLD observed in the occipital lobe during visual stimulation. In this study, the metabolic demand of such a response was studied by measuring local metabolite concentration changes during a visual checkerboard stimulation using functional magnetic resonance spectroscopy (fMRS) at 7 Tesla. The results showed increases of glutamate and lactate concentrations during the positive BOLD response, consistent with previous fMRS studies. In contrast, during the negative BOLD response, decreasing concentrations of glutamate, lactate and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) were found, suggesting a reduction of glycolytic and oxidative metabolic demand below the baseline. Additionally, the respective changes of the BOLD signal, glutamate and lactate concentrations of both groups suggest that a local increase of inhibitory activity might occur during the negative BOLD response.
Keywords: Functional magnetic resonance imaging; brain metabolism; functional magnetic resonance spectroscopy; inhibition; negative blood oxygenation–level dependent; neurovascular coupling; positive blood oxygenation–level dependent; visual stimulation.
Figures
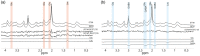


References
-
- Logothetis NK, Pauls J, Augath M, et al.Neurophysiological investigation of the basis of the fMRI signal. Nature 2001; 412: 150–157. - PubMed
-
- Tootell RB, Hadjikhani N, Hall EK, et al.The retinotopy of visual spatial attention. Neuron 1998; 21: 1409–1422. - PubMed
-
- Laurienti PJ, Burdette JH, Wallace MT, et al.Deactivation of sensory-specific cortex by cross-modal stimuli. J Cogn Neurosci 2002; 14: 420–429. - PubMed
-
- Harel N, Lee S-P, Nagaoka T, et al.Origin of negative blood oxygenation level-dependent fMRI signals. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2002; 22: 908–917. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

