Combined Aurora Kinase A (AURKA) and WEE1 Inhibition Demonstrates Synergistic Antitumor Effect in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck
- PMID: 30755439
- PMCID: PMC6548643
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-0440
Combined Aurora Kinase A (AURKA) and WEE1 Inhibition Demonstrates Synergistic Antitumor Effect in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck
Abstract
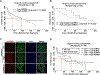
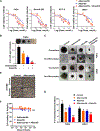
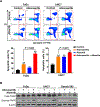
Purpose: Human papillomavirus (HPV)-negative head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCC) commonly bear disruptive mutations in TP53, resulting in treatment resistance. In these patients, direct targeting of p53 has not been successful, but synthetic lethal approaches have promise. Although Aurora A kinase (AURKA) is overexpressed and an oncogenic driver, its inhibition has only modest clinical effects in HPV-negative HNSCC. We explored a novel combination of AURKA and WEE1 inhibition to overcome intrinsic resistance to AURKA inhibition.Experimental Design: AURKA protein expression was determined by fluorescence-based automated quantitative analysis of patient specimens and correlated with survival. We evaluated treatment with the AURKA inhibitor alisertib (MLN8237) and the WEE1 inhibitor adavosertib (AZD1775), alone or in combination, using in vitro and in vivo HNSCC models.
Results: Elevated nuclear AURKA correlated with worse survival among patients with p16(-) HNSCC. Alisertib caused spindle defects, G2-M arrest and inhibitory CDK1 phosphorylation, and cytostasis in TP53 mutant HNSCC FaDu and UNC7 cells. Addition of adavosertib to alisertib instead triggered mitotic entry and mitotic catastrophe. Moreover, in FaDu and Detroit 562 xenografts, this combination demonstrated synergistic effects on tumor growth and extended overall survival compared with either vehicle or single-agent treatment.
Conclusions: Combinatorial treatment with adavosertib and alisertib leads to synergistic antitumor effects in in vitro and in vivo HNSCC models. These findings suggest a novel rational combination, providing a promising therapeutic avenue for TP53-mutated cancers.
©2019 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Combined Inhibition of Rad51 and Wee1 Enhances Cell Killing in HNSCC Through Induction of Apoptosis Associated With Excessive DNA Damage and Replication Stress.Mol Cancer Ther. 2021 Jul;20(7):1257-1269. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-20-0252. Epub 2021 May 4. Mol Cancer Ther. 2021. PMID: 33947685 Free PMC article.
-
Wee-1 Kinase Inhibition Sensitizes High-Risk HPV+ HNSCC to Apoptosis Accompanied by Downregulation of MCl-1 and XIAP Antiapoptotic Proteins.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Nov 1;21(21):4831-44. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0279. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26124202 Free PMC article.
-
Concurrent Inhibition of Neurosphere and Monolayer Cells of Pediatric Glioblastoma by Aurora A Inhibitor MLN8237 Predicted Survival Extension in PDOX Models.Clin Cancer Res. 2018 May 1;24(9):2159-2170. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2256. Epub 2018 Feb 20. Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29463553 Free PMC article.
-
An update on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of alisertib, a selective Aurora kinase A inhibitor.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016 Jun;43(6):585-601. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12571. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26999067 Review.
-
WEE1 inhibition in cancer therapy: Mechanisms, synergies, preclinical insights, and clinical trials.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2025 Jul;211:104710. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2025.104710. Epub 2025 Apr 3. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2025. PMID: 40187712 Review.
Cited by
-
Aurora kinase A inhibition induces synthetic lethality in SMAD4-deficient colorectal cancer cells via spindle assembly checkpoint activation.Oncogene. 2022 May;41(19):2734-2748. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02293-y. Epub 2022 Apr 7. Oncogene. 2022. PMID: 35393542
-
Combined TRIP13 and Aurora Kinase Inhibition Induces Apoptosis in Human Papillomavirus-Driven Cancers.Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Oct 14;28(20):4479-4493. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-1627. Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35972731 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Histone Epigenetic Modifications and DNA Damage Responses in Synthetic Lethality Strategies in Cancer?Cancers (Basel). 2022 Aug 22;14(16):4050. doi: 10.3390/cancers14164050. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36011043 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Updates on Oncogenic Signaling of Aurora Kinases in Chemosensitive, Chemoresistant Cancers: Novel Medicinal Chemistry Approaches for Targeting Aurora Kinases.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(23):3502-3528. doi: 10.2174/0929867330666230503124408. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37138483 Review.
-
Identification of Wee1 as a target in combination with avapritinib for gastrointestinal stromal tumor treatment.JCI Insight. 2021 Jan 25;6(2):e143474. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.143474. JCI Insight. 2021. PMID: 33320833 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin 2017;67:7–30. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

