Quantitative phosphoproteomics reveals mitotic function of the ATR activator ETAA1
- PMID: 30755469
- PMCID: PMC6446857
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201810058
Quantitative phosphoproteomics reveals mitotic function of the ATR activator ETAA1
Abstract
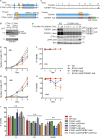
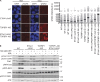
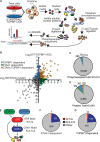
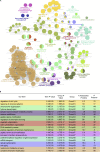
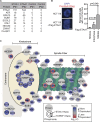
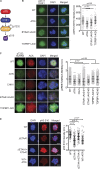
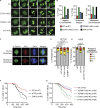
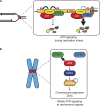
The ATR kinase controls cell cycle transitions and the DNA damage response. ATR activity is regulated through two ATR-activating proteins, ETAA1 and TOPBP1. To examine how each activator contributes to ATR signaling, we used quantitative mass spectrometry to identify changes in protein phosphorylation in ETAA1- or TOPBP1-deficient cells. We identified 724, 285, and 118 phosphosites to be regulated by TOPBP1, ETAA1, or both ATR activators, respectively. Gene ontology analysis of TOPBP1- and ETAA1-dependent phosphoproteins revealed TOPBP1 to be a primary ATR activator for replication stress, while ETAA1 regulates mitotic ATR signaling. Inactivation of ATR or ETAA1, but not TOPBP1, results in decreased Aurora B kinase activity during mitosis. Additionally, ATR activation by ETAA1 is required for proper chromosome alignment during metaphase and for a fully functional spindle assembly checkpoint response. Thus, we conclude that ETAA1 and TOPBP1 regulate distinct aspects of ATR signaling with ETAA1 having a dominant function in mitotic cells.
© 2019 Bass and Cortez.
Figures

Comment in
-
ETAA1 ensures proper chromosome segregation: A matter of S phase or mitosis?J Cell Biol. 2019 Dec 2;218(12):3883-3884. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201910157. Epub 2019 Nov 4. J Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31685532 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bindea G., Mlecnik B., Hackl H., Charoentong P., Tosolini M., Kirilovsky A., Fridman W.-H., Pagès F., Trajanoski Z., and Galon J.. 2009. ClueGO: a Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics. 25:1091–1093. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp101 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

