Repression of Human Papillomavirus Oncogene Expression under Hypoxia Is Mediated by PI3K/mTORC2/AKT Signaling
- PMID: 30755508
- PMCID: PMC6372795
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.02323-18
Repression of Human Papillomavirus Oncogene Expression under Hypoxia Is Mediated by PI3K/mTORC2/AKT Signaling
Abstract
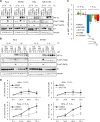
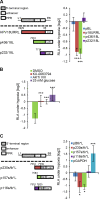
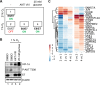
Hypoxia is linked to therapeutic resistance and poor clinical prognosis for many tumor entities, including human papillomavirus (HPV)-positive cancers. Notably, HPV-positive cancer cells can induce a dormant state under hypoxia, characterized by a reversible growth arrest and strong repression of viral E6/E7 oncogene expression, which could contribute to therapy resistance, immune evasion and tumor recurrence. The present work aimed to gain mechanistic insights into the pathway(s) underlying HPV oncogene repression under hypoxia. We show that E6/E7 downregulation is mediated by hypoxia-induced stimulation of AKT signaling. Ablating AKT function in hypoxic HPV-positive cancer cells by using chemical inhibitors efficiently counteracts E6/E7 repression. Isoform-specific activation or downregulation of AKT1 and AKT2 reveals that both AKT isoforms contribute to hypoxic E6/E7 repression and act in a functionally redundant manner. Hypoxic AKT activation and consecutive E6/E7 repression is dependent on the activities of the canonical upstream AKT regulators phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) complex 2 (mTORC2). Hypoxic downregulation of E6/E7 occurs, at least in part, at the transcriptional level. Modulation of E6/E7 expression by the PI3K/mTORC2/AKT cascade is hypoxia specific and not observed in normoxic HPV-positive cancer cells. Quantitative proteome analyses identify additional factors as candidates to be involved in hypoxia-induced activation of the PI3K/mTORC2/AKT signaling cascade and in the AKT-dependent repression of the E6/E7 oncogenes under hypoxia. Collectively, these data uncover a functional key role of the PI3K/mTORC2/AKT signaling cascade for viral oncogene repression in hypoxic HPV-positive cancer cells and provide new insights into the poorly understood cross talk between oncogenic HPVs and their host cells under hypoxia.IMPORTANCE Oncogenic HPV types are major human carcinogens. Under hypoxia, HPV-positive cancer cells can repress the viral E6/E7 oncogenes and induce a reversible growth arrest. This response could contribute to therapy resistance, immune evasion, and tumor recurrence upon reoxygenation. Here, we uncover evidence that HPV oncogene repression is mediated by hypoxia-induced activation of canonical PI3K/mTORC2/AKT signaling. AKT-dependent downregulation of E6/E7 is only observed under hypoxia and occurs, at least in part, at the transcriptional level. Quantitative proteome analyses identify additional factors as candidates to be involved in AKT-dependent E6/E7 repression and/or hypoxic PI3K/mTORC2/AKT activation. These results connect PI3K/mTORC2/AKT signaling with HPV oncogene regulation, providing new mechanistic insights into the cross talk between oncogenic HPVs and their host cells.
Keywords: AKT; cervical cancer; human papillomavirus; tumor virus.
Copyright © 2019 Bossler et al.
Figures




Similar articles
-
PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Regulates the Virus/Host Cell Crosstalk in HPV-Positive Cervical Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 3;20(9):2188. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092188. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31058807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of dormancy in hypoxic human papillomavirus-positive cancer cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Feb 7;114(6):E990-E998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1615758114. Epub 2017 Jan 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28115701 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Metformin on the virus/host cell crosstalk in human papillomavirus-positive cancer cells.Int J Cancer. 2021 Sep 1;149(5):1137-1149. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33594. Epub 2021 May 6. Int J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33844847
-
The Human Papillomavirus 16 E7 Oncoprotein Attenuates AKT Signaling To Promote Internal Ribosome Entry Site-Dependent Translation and Expression of c-MYC.J Virol. 2016 May 27;90(12):5611-5621. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00411-16. Print 2016 Jun 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27030265 Free PMC article.
-
The HPV E6/E7 Oncogenes: Key Factors for Viral Carcinogenesis and Therapeutic Targets.Trends Microbiol. 2018 Feb;26(2):158-168. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2017.07.007. Epub 2017 Aug 17. Trends Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 28823569 Review.
Cited by
-
Linking Cancer Stem Cell Plasticity to Therapeutic Resistance-Mechanism and Novel Therapeutic Strategies in Esophageal Cancer.Cells. 2020 Jun 17;9(6):1481. doi: 10.3390/cells9061481. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32560537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p63 Directs Subtype-Specific Gene Expression in HPV+ Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 May 31;12:879054. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.879054. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35712470 Free PMC article.
-
PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Regulates the Virus/Host Cell Crosstalk in HPV-Positive Cervical Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 3;20(9):2188. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092188. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31058807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of hypoxia on antigen presentation and T cell-based immune recognition of HPV16-transformed cells.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 21;13:918528. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.918528. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36341354 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxic HPV-Positive Cancer Cells Are Particularly Sensitive to the Pro-Senescent Effects of B-MYB Repression Due to the Lack of Compensatory A-MYB Induction.J Med Virol. 2025 Jun;97(6):e70422. doi: 10.1002/jmv.70422. J Med Virol. 2025. PMID: 40444458 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

