KIAA1199 is a secreted molecule that enhances osteoblastic stem cell migration and recruitment
- PMID: 30755597
- PMCID: PMC6372631
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-018-1202-9
KIAA1199 is a secreted molecule that enhances osteoblastic stem cell migration and recruitment
Abstract
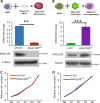
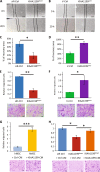
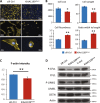
Factors mediating mobilization of osteoblastic stem and progenitor cells from their bone marrow niche to be recruited to bone formation sites during bone remodeling are poorly known. We have studied secreted factors present in the bone marrow microenvironment and identified KIAA1199 (also known as CEMIP, cell migration inducing hyaluronan binding protein) in human bone biopsies as highly expressed in osteoprogenitor reversal cells (Rv.C) recruited to the eroded surfaces (ES), which are the future bone formation sites. In vitro, KIAA1199 did not affect the proliferation of human osteoblastic stem cells (also known as human bone marrow skeletal or stromal stem cells, hMSCs); but it enhanced cell migration as determined by scratch assay and trans-well migration assay. KIAA1199 deficient hMSCs (KIAA1199down) exhibited significant changes in cell size, cell length, ratio of cell width to length and cell roundness, together with reduction of polymerization actin (F-actin) and changes in phos-CFL1 (cofflin1), phos-LIMK1 (LIM domain kinase 1) and DSTN (destrin), key factors regulating actin cytoskeletal dynamics and cell motility. Moreover, KIAA1199down hMSC exhibited impaired Wnt signaling in TCF-reporter assay and decreased expression of Wnt target genes and these effects were rescued by KIAA1199 treatment. Finally, KIAA1199 regulated the activation of P38 kinase and its associated changes in Wnt-signaling. Thus, KIAA1199 is a mobilizing factor that interacts with P38 and Wnt signaling, and induces changes in actin cytoskeleton, as a mechanism mediating recruitment of hMSC to bone formation sites.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Inhibiting actin depolymerization enhances osteoblast differentiation and bone formation in human stromal stem cells.Stem Cell Res. 2015 Sep;15(2):281-9. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2015.06.009. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Stem Cell Res. 2015. PMID: 26209815
-
KIAA1199 deficiency enhances skeletal stem cell differentiation to osteoblasts and promotes bone regeneration.Nat Commun. 2023 Apr 10;14(1):2016. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37651-1. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37037828 Free PMC article.
-
LIM kinase 1 - dependent cofilin 1 pathway and actin dynamics mediate nuclear retinoid receptor function in T lymphocytes.BMC Mol Biol. 2011 Sep 16;12:41. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-12-41. BMC Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21923909 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of KIAA1199 in cancer development and therapy.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Jun;138:111507. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111507. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33773462 Review.
-
The Role of LIM Kinase in the Male Urogenital System.Cells. 2021 Dec 28;11(1):78. doi: 10.3390/cells11010078. Cells. 2021. PMID: 35011645 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aggrecan and Hyaluronan: The Infamous Cartilage Polyelectrolytes - Then and Now.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1402:3-29. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-25588-5_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37052843
-
Molecular Biomarkers of Canine Reproductive Functions.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jun 17;46(6):6139-6168. doi: 10.3390/cimb46060367. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38921038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide investigation of lncRNAs revealed their tight association with gastric cancer.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 May 18;150(5):261. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05790-7. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38761291 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial Organization of Osteoclastic Coupling Factors and Their Receptors at Human Bone Remodeling Sites.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Jun 14;9:896841. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.896841. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35775083 Free PMC article.
-
Serum KIAA1199 is an advanced-stage prognostic biomarker and metastatic oncogene in cholangiocarcinoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Nov 10;12(23):23761-23777. doi: 10.18632/aging.103964. Epub 2020 Nov 10. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 33197891 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

