Endocan as a marker of microvascular inflammation in kidney transplant recipients
- PMID: 30755622
- PMCID: PMC6372712
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-37975-9
Endocan as a marker of microvascular inflammation in kidney transplant recipients
Abstract
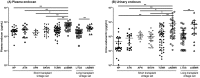
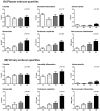
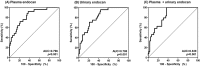
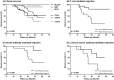
Endocan is a water-soluble proteoglycan exclusively secreted by vascular endothelium. Endocan levels may be elevated in kidney transplant recipients experiencing antibody-mediated rejection (ABMR), which is characterized by vascular inflammation in transplanted kidney. We evaluated the clinical relevance of endocan as markers of microvascular inflammation in patients who underwent kidney transplantation. Plasma and urinary endocan levels were measured in 203 kidney transplant recipients and were compared across different etiologies of allograft dysfunction and various pathologic scores. Both plasma and urinary endocan levels were significantly higher in patients with acute ABMR than those in patients with normal pathology, acute tubular necrosis (ATN), acute pyelonephritis, BK virus associated nephropathy (BKVN), and T-cell mediated rejection (TCMR). Patients with chronic active ABMR also exhibited significantly higher plasma and urinary endocan levels than patients with long-term graft survival. Scores of glomerulitis and peritubular capillaritis, which are typical features of microvascular inflammation, were significantly elevated in patients with higher plasma and/or urinary endocan levels. Furthermore, plasma and urinary endocan levels could effectively discriminate ABMR from ATN, BKVN, and TCMR. Finally, patients exhibiting high urinary and plasma endocan levels in acute ABMR group showed significantly worse renal survival. Altogether, plasma and urinary endocan levels may serve as potential markers of microvascular inflammation in kidney transplant recipients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

