Differential PI(4,5)P2 sensitivities of TRPC4, C5 homomeric and TRPC1/4, C1/5 heteromeric channels
- PMID: 30755645
- PMCID: PMC6372716
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-38443-0
Differential PI(4,5)P2 sensitivities of TRPC4, C5 homomeric and TRPC1/4, C1/5 heteromeric channels
Abstract
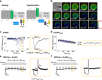
Transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC) 4 and TRPC5 channels are modulated by the Gαq-PLC pathway. Since phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P2) maintains TRPC4 and TRPC5 channel function, the Gαq-PLC pathway inhibits channel activity by depleting PI(4,5)P2. Here we investigated the difference in PI(4,5)P2 sensitivity between homomeric and heteromeric TRPC channels. First, by using a Danio rerio voltage-sensing phosphatase (DrVSP), we show that PI(4,5)P2 dephosphorylation robustly inhibits TRPC4α, TRPC4β, and TRPC5 homotetramer currents and also TRPC1/4α, TRPC1/4β, and TRPC1/5 heterotetramer currents. Secondly, sensitivity of channels to PI(4,5)P2 dephosphorylation was suggested through the usage of FRET in combination with patch clamping. The sensitivity increased in the sequence TRPC4β < TRPC4α < TRPC5 in homotetramers, whereas when forming heterotetramers with TRPC1, the sensitivity was approximately equal between the channels. Thirdly, we determined putative PI(4,5)P2 binding sites based on a TRPC4 prediction model. By neutralization of basic residues, we identified putative PI(4,5)P2 binding sites because the mutations reduced FRET to a PI(4,5)P2 sensor and reduced the current amplitude. Therefore, one functional TRPC4 has 8 pockets with the two main binding regions; K419, K664/R511, K518, H630. We conclude that TRPC1 channel function as a regulator in setting PI(4,5)P2 affinity for TRPC4 and TRPC5 that changes PI(4,5)P2 sensitivity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

