Cdh2 coordinates Myosin-II dependent internalisation of the zebrafish neural plate
- PMID: 30755665
- PMCID: PMC6372647
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-38455-w
Cdh2 coordinates Myosin-II dependent internalisation of the zebrafish neural plate
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Cdh2 coordinates Myosin-II dependent internalisation of the zebrafish neural plate.Sci Rep. 2019 May 17;9(1):7699. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43789-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31097745 Free PMC article.
Abstract
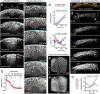
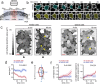
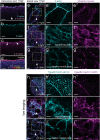
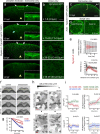
Tissue internalisation is a key morphogenetic mechanism by which embryonic tissues generate complex internal organs and a number of studies of epithelia have outlined a general view of tissue internalisation. Here we have used quantitative live imaging and mutant analysis to determine whether similar mechanisms are responsible for internalisation in a tissue that apparently does not have a typical epithelial organisation - the zebrafish neural plate. We found that although zebrafish embryos begin neurulation without a conventional epithelium, medially located neural plate cells adopt strategies typical of epithelia in order to constrict their dorsal surface membrane during cell internalisation. Furthermore, we show that Myosin-II activity is a significant driver of this transient cell remodeling which also depends on Cdh2 (N-cadherin). Abrogation of Cdh2 results in defective Myosin-II distribution, mislocalised internalisation events and defective neural plate morphogenesis. Our work suggests Cdh2 coordinates Myosin-II dependent internalisation of the zebrafish neural plate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Sweeton D, Parks S, Costa M, Wieschaus E. Gastrulation in Drosophila: the formation of the ventral furrow and posterior midgut invaginations. Development. 1991;112:775–89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

