Tumour necrosis factor signalling in health and disease
- PMID: 30755793
- PMCID: PMC6352924
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.17023.1
Tumour necrosis factor signalling in health and disease
Abstract
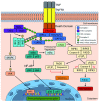
The master pro-inflammatory cytokine, tumour necrosis factor (TNF), has been shown to modulate multiple signalling pathways, with wide-ranging downstream effects. TNF plays a vital role in the typical immune response through the regulation of a number of pathways encompassing an immediate inflammatory reaction with significant innate immune involvement as well as cellular activation with subsequent proliferation and programmed cell death or necrosis. As might be expected with such a broad spectrum of cellular effects and complex signalling pathways, TNF has also been implicated in a number of disease states, such as rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and Crohn's disease. Since the time of its discovery over 40 years ago, TNF ligand and its receptors, TNF receptor (TNFR) 1 and 2, have been categorised into two complementary superfamilies, namely TNF (TNFSF) and TNFR (TNFRSF), and 19 ligands and 29 receptors have been identified to date. There have been significant advances in our understanding of TNF signalling pathways in the last decade, and this short review aims to elucidate some of the most recent advances involving TNF signalling in health and disease.
Keywords: Autoinflammatory; Cell death; Immunometabolism; TNF; TNFR.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.No competing interests were disclosed.No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

