Type II Renal Tubular Acidosis Secondary to Topiramate: A Review
- PMID: 30755834
- PMCID: PMC6351003
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.3635
Type II Renal Tubular Acidosis Secondary to Topiramate: A Review
Abstract
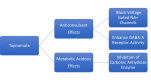
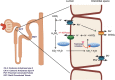
Topiramate (TMP) is a broad-spectrum anticonvulsant drug used to treat a wide variety of seizure disorders, for migraine prophylaxis, and for many other indications. An important side effect of TMP is metabolic acidosis, which is mediated by renal tubular defects. TMP inhibits carbonic anhydrase, an enzyme that is necessary for acid handling in the proximal renal tubule. Patients can present with asymptomatic serum electrolyte derangements, acute change in mental status, hyperventilation, cardiac arrhythmias, or other sequelae of metabolic acidosis and associated respiratory compensation. If taken chronically, TMP can cause renal stone formation, bone mineralization defects, and several other effects secondary to changes in serum and urine pH and electrolytes. There is no well-studied way to prevent metabolic acidosis in patients taking TMP, but physicians should be vigilant when prescribing this drug to patients with the history of renal diseases and other comorbidities, and aware of this potential etiology of metabolic acidosis. We present a literature review of the underlying mechanisms involved in the development of renal tubular acidosis secondary to TMP and its clinical consequences.
Keywords: renal tubular acidosis; topiramate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Topiramate and metabolic acidosis: an evolving story.Hosp Pract (1995). 2017 Dec;45(5):192-195. doi: 10.1080/21548331.2017.1370969. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Hosp Pract (1995). 2017. PMID: 28828886
-
Effect of topiramate on acid-base balance: extent, mechanism and effects.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009 Nov;68(5):655-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2009.03521.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19916989 Free PMC article.
-
Presumptive renal tubular acidosis secondary to topiramate administration in a cat.J Vet Emerg Crit Care (San Antonio). 2022 May;32(3):420-425. doi: 10.1111/vec.13168. Epub 2022 Feb 10. J Vet Emerg Crit Care (San Antonio). 2022. PMID: 35142423
-
Narrative Review of Topiramate: Clinical Uses and Pharmacological Considerations.Adv Ther. 2023 Sep;40(9):3626-3638. doi: 10.1007/s12325-023-02586-y. Epub 2023 Jun 27. Adv Ther. 2023. PMID: 37368102 Review.
-
Evaluation of carbonic anhydrase isozymes in disorders involving osteopetrosis and/or renal tubular acidosis.Clin Biochem. 1991 Aug;24(4):311-8. doi: 10.1016/0009-9120(91)80005-n. Clin Biochem. 1991. PMID: 1959222 Review.
Cited by
-
The therapeutic importance of acid-base balance.Biochem Pharmacol. 2021 Jan;183:114278. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114278. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33039418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A narrative review of the importance of pharmacokinetics and drug-drug interactions of preventive therapies in migraine management.Headache. 2021 Jun;61(6):838-853. doi: 10.1111/head.14135. Headache. 2021. PMID: 34214182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Topiramate causing type II renal tubular acidosis: A case and review of the mechanism.Clin Case Rep. 2020 Feb 18;8(4):731-733. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.2733. eCollection 2020 Apr. Clin Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32274047 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Efficacy and tolerability of the new antiepileptic drugs II: treatment of refractory epilepsy. Report of the Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee and Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Epilepsy Society. French JA, Kanner AM, Bautista J, et al. Neurology. 2004;62:1261–1273. - PubMed
-
- Clinical efficacy of topiramate as add‐on therapy in refractory partial epilepsy: the European experience. Ben‐Menachem E. Epilepsia. 1997;38:0. - PubMed
-
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA). FDA labelling information. [Nov;2018 ];http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/drugsatfda/index.cfm 2018
-
- New and future migraine therapy. Ramadan NM, Buchanan TM. Pharmacol Ther. 2006;112:199–212. - PubMed
-
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors as emerging drugs for the treatment of obesity. Supuran CT, Di Fiore A, De Simone G. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2008;13:383–392. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources