Acute Q Fever Presenting with Multi-Organ Failure: Re-Evaluation of the Initial Diagnosis
- PMID: 30755876
- PMCID: PMC6346862
- DOI: 10.12890/2016_000423
Acute Q Fever Presenting with Multi-Organ Failure: Re-Evaluation of the Initial Diagnosis
Abstract
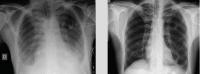
We present the case of a 48-year-old man admitted to the critical care unit with atrial fibrillation, and acute heart and kidney failure accompanied by coagulopathy and an abnormal liver test. Initially diagnosed as a non-ST elevation myocardial infarction, re-evaluation of the case led to the consideration of severe sepsis. Q fever and leptospirosis were the most probable causes and empiric treatment was initiated. A complete recovery was achieved following treatment.
Learning points: Epidemiological antecedents of interest must always be collected in the clinical record.Acute Q fever infection may be mild or present with multiple organ damage.Empiric treatment with doxycycline must be started when Q fever is suspected.
Keywords: Q fever; Raw milk; multiorgan failure.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interests: The Authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Suárez Ortega S, Coello García I, Rodríguez Fernández JM, Arkuch Saade ME, Sanz Peláez O, Betancor León P. Miocarditis por Fiebre Q: presentación de un caso. Mapfre Med. 2005;16:223–227.
-
- Suárez Ortega S, Rivero Vera J, Hemmersbach M, Artiles Campelo F, Reyes Pérez R. Betancor León P. Hepatitis colestásica grave por fiebre Q: presentación de un caso. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;33:21–24. - PubMed
-
- Anderson A, Bijlmer H, Fournier PE, Graves S, Hartzell J, Kersh GJ, et al. Diagnosis and manage-ment of Q fever--United States, 2013: recommendations from CDC and the Q Fever Working Group. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2013;62(RR-03):1–30. - PubMed
-
- Somasundaram R, Loddenkemper C, Zeitz M, Schneider T. A souvenir from the Canary Islands. Lancet. 2006;367:1116. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources