Pulmonary Mucormycosis (Zygomycosis) Presenting as an Infective Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- PMID: 30756000
- PMCID: PMC6346968
- DOI: 10.12890/2018_000995
Pulmonary Mucormycosis (Zygomycosis) Presenting as an Infective Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Abstract
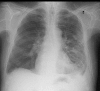
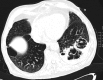
Mucormycosis is a life-threatening fungal infection whose incidence has been rising recently, mainly due to the increasing use of immunosuppressive and corticosteroid treatment. In previous decades, mucormycosis was associated with a very poor prognosis as mortality was approximately 100%. Mortality rates reported in recent literature have only slightly improved despite the availability of targeted therapy with amphotericin B. Pulmonary mucormycosis is characteristically encountered in severely immunocompromised hosts, while rhino-orbital disease is often seen in individuals with diabetes mellitus. We report a rare case of fulminant pulmonary mucormycosis as an exceptionally rare complication of corticosteroid treatment in a 76-year-old patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and diabetes. The patient had presented with typical symptoms of an infective COPD exacerbation. The interesting aspects of our case were the absence of malignancy or immunosuppression, the isolation of Rhizomucor species, and the fungal invasion of the pleura and pericardium. Unfortunately, our patient died on the 49th day of hospitalisation, despite appropriate treatment.
Learning points: Pulmonary mucormycosis in patients with known respiratory disease may mimic an exacerbation of their lung disease, thus delaying diagnosis.Pulmonary mucormycosis can complicate corticosteroid treatment in elderly individuals with other predisposing factors, which is an emerging clinical concern.Pulmonary mucormycosis remains a potentially fatal disease, although early diagnosis and appropriate medical and surgical management can improve outcomes.
Keywords: Mucormycosis; Rhizomucor; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; diabetes mellitus; zygomycosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interests: The Authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Smith JA, Kauffman CA. Pulmonary fungal infections. Respirology. 2012;17:913–926. - PubMed
-
- Roden MM, Zaoutis TE, Buchanan WL, Knudsen TA, Sarkisova TA, Schaufele RL, et al. Epidemiology and outcome of zygomycosis: a review of 929 reported cases. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;42:634–653. - PubMed
-
- Skiada A, Pagano L, Groll A, Zimmerli S, Dupont B, Lagrou K, et al. Zygomycosis in Europe: analysis of 230 cases accrued by the registry of the European Confederation of Medical Mycology (ECMM) working group on zygomycosis between 2005 and 2007. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011;17:1859–1867. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
