Radiofrequency phase encoded half-pulses in simultaneous multislice ultrashort echo time imaging
- PMID: 30756426
- PMCID: PMC6435423
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.27693
Radiofrequency phase encoded half-pulses in simultaneous multislice ultrashort echo time imaging
Abstract
Purpose: To describe a simultaneous multislice (SMS) ultrashort echo time (UTE) imaging method using radiofrequency phase encoded half-pulses in combination with power independent of number of slices (PINS) inversion recovery (IR) pulses to generate multiple-slice images with short T2 * contrasts in less than 3 min with close to an eightfold acceleration compared with a standard 2D approach.
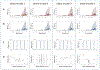
Theory and methods: Radiofrequency phase encoding is applied in an SMS (NSMS = 4) excitation scheme using "sinc" half-pulses. With the use of coil sensitivity encoding (SENSE) and controlled aliasing in parallel imaging (CAIPI) in combination with a gradient echo 2D spiral readout trajectory and IR PINS pulses for contrast enhancement a fast UTE sequence is developed. Images are obtained using a model-based reconstruction method. Sequence details and performance tests on phantoms as well as the heads of healthy volunteers at 3T are presented.
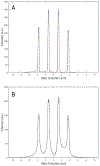
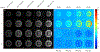
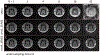
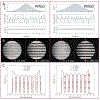
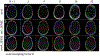
Results: An SMS UTE sequence with an undersampling factor of 4 is developed using radiofrequency phase encoded half-pulses and PINS IR pulses which enables the acquisition of 8 slices at 0.862 mm2 resolution in less than 3-min scan time. UTE images of the head are obtained showing highlighted signal of cortical bone. Image quality and T2 contrast are comparable to the one obtained by corresponding single slice acquisitions with only minor deviations.
Conclusions: The method combining radiofrequency phase encoded SMS half-pulses and PINS IR pulses presents a suitable approach to SMS UTE imaging. The usage of coil sensitivity information and increased sampling density by means of interleaved slice group acquisitions allows to reduce the total scan time by a factor close to 8.
Keywords: CAIPI; PINS; SMS; UTE; half-pulse; simultaneous multislice excitation; ultrashort echo time imaging.
© 2019 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures


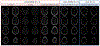
References
-
- Martyn P MRI of tissues with short T2s and T2*s. G. M. Bydder, G. D. Fullerton and I. R. Young. NMR in biomedicine 2013;26(10):1336–1337.
-
- Gatehouse PD, Bydder GM. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Short T2 Components in Tissue. Clinical radiology 2003;58(1):1–19. - PubMed
-
- MD P, LI J. Ultra-fast imaging using low flip angles and fids. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 1995;34(4):525–529. - PubMed
-
- GD M, JP M, Bjoern H Ultrashort echo time imaging using pointwise encoding time reduction with radial acquisition (PETRA). Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 2012;67(2):510–518. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

