Osteopontin counters human immunodeficiency virus type 1-induced impairment of neurite growth through mammalian target of rapamycin and beta-integrin signaling pathways
- PMID: 30758811
- PMCID: PMC6647884
- DOI: 10.1007/s13365-019-00729-y
Osteopontin counters human immunodeficiency virus type 1-induced impairment of neurite growth through mammalian target of rapamycin and beta-integrin signaling pathways
Abstract
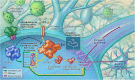
Despite the fact that human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) does not enter or replicate in neurons, its infection of a subset of resident brain glia cells (microglia and astrocytes) induces via disparate mechanisms, dysregulation of glutamate metabolism, neurotoxicity, and inflammation. Antiretroviral therapies suppress viral load, but cellular activation and release of proinflammatory factors, some of which is likely related to viral reservoirs, continue to promote a microenvironment that is injurious to neurons. However, the molecular mechanisms remain to be identified. Osteopontin (OPN) is a proinflammatory cytokine-like, extracellular matrix protein that is elevated within the brain and CSF in several neurodegenerative disorders, including HIV-associated cognitive disorder. However, the impact of elevated OPN on neuronal integrity and function in HIV-infected individuals who exhibit cognitive dysfunction remains unknown. In this study, using a neuronal cell line and primary cultures of cortical rat neurons, we identify the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway involvement in a signaling interaction between OPN-β1-integrins and the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein, which stimulates neurite growth. These findings link for the first time HIV X4-envelope receptor engagement and osteopontin-mediated signaling through β1-integrin receptors to the mTOR pathway and alterations in the cytoskeleton of cortical neurons.
Keywords: Cytoskeleton; Dendrites; HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder; Integrins; Neurons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Microglial- neuronal crosstalk in chronic viral infection through mTOR, SPP1/OPN and inflammasome pathway signaling.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 5;15:1368465. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1368465. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38646526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cortical neurons are a prominent source of the proinflammatory cytokine osteopontin in HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders.J Neurovirol. 2015 Apr;21(2):174-85. doi: 10.1007/s13365-015-0317-3. Epub 2015 Jan 31. J Neurovirol. 2015. PMID: 25636782 Free PMC article.
-
Osteopontin and Integrin Mediated Modulation of Post-Synapses in HIV Envelope Glycoprotein Exposed Hippocampal Neurons.Brain Sci. 2020 Jun 4;10(6):346. doi: 10.3390/brainsci10060346. Brain Sci. 2020. PMID: 32512754 Free PMC article.
-
Osteopontin is upregulated after mechanical brain injury and stimulates neurite growth from hippocampal neurons through β1 integrin and CD44.Neuroreport. 2012 Aug 1;23(11):647-52. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0b013e328355380e. Neuroreport. 2012. PMID: 22692550
-
Macrophages, chemokines and neuronal injury in HIV-1-associated dementia.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2002 Mar;48(2):137-50. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2002. PMID: 11995633 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrin Signaling in the Central Nervous System in Animals and Human Brain Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 27;23(3):1435. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031435. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro models of HIV-1 infection of the Central Nervous System.Drug Discov Today Dis Models. 2020 Fall;32(Pt A):5-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ddmod.2019.10.007. Epub 2019 Dec 20. Drug Discov Today Dis Models. 2020. PMID: 33692833 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of mTORC1 Signaling Pathway by HIV-1.Cells. 2020 Apr 28;9(5):1090. doi: 10.3390/cells9051090. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32354054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with serious mental illness and possible benefits of prophylaxis with Memantine and Amantadine.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2020 Oct-Dec;61(4):1007-1022. doi: 10.47162/RJME.61.4.03. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2020. PMID: 34171050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglial- neuronal crosstalk in chronic viral infection through mTOR, SPP1/OPN and inflammasome pathway signaling.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 5;15:1368465. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1368465. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38646526 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Antinori A, Arendt G, Becker JT, Brew BJ, Byrd DA, Cherner M, Clifford DB, Cinque P, Epstein LG, Goodkin K, Gisslen M, Grant I, Heaton RK, Joseph J, Marder K, Marra CM, McArthur JC, Nunn M, Price RW, Pulliam L, Robertson KR, Sacktor N, Valcour V, Wojna VE. Updated research nosology for HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. Neurology. 2007;69:1789–1799. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Asjo B, Morfeldt-Manson L, Albert J, Biberfeld G, Karlsson A, Lidman K, Fenyo EM. Replicative capacity of human immunodeficiency virus from patients with varying severity of HIV infection. Lancet. 1986;2:660–662. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

