Therapeutic effect of double plasma molecular adsorption system and sequential half-dose plasma exchange in patients with HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure
- PMID: 30758886
- PMCID: PMC6767528
- DOI: 10.1002/jca.21690
Therapeutic effect of double plasma molecular adsorption system and sequential half-dose plasma exchange in patients with HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure
Abstract
Objective: The artificial liver support system (ALSS) is used frequently as a first-line treatment for hepatitis B virus-associated acute-on-chronic liver failure (HBV-ACLF). This study aims to compare the therapeutic efficacy of double plasma molecular adsorption system (DPMAS) with sequential half-dose plasma exchange (PE) (DPMAS+PE) and full-dose PE in patients with HBV-ACLF.
Methods: A total of 131 hospitalized patients who were diagnosed with HBV-ACLF and underwent DPMAS+PE or PE were retrospectively analyzed. According to the treatment methods used, they were divided into PE group (n = 77) and DPMAS+PE group (n = 54). The main evaluation indexes included the change of liver function and the 28-days liver transplant-free survival rates after the different treatments.
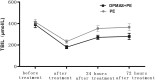
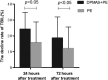
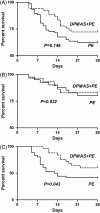
Results: There were no significant differences on severity of illness between PE group and DPMAS+PE group (P > 0.05). The total bilirubin (TBIL) levels immediately after treatment, and at 24 and 72 hours after treatment were markedly decreased in DPMAS+PE group than that in PE group (52.3 ± 9.4% vs 42.3 ± 7.2%, P < 0.05; 24.2 ± 10.0% vs 13.5 ± 13.0%, P < 0.05; 24.8 ± 13.1% vs 14.9 ± 14.9%, P < 0.05; respectively). The 28-days survival rates was 62.3% and 72.2% in PE and DPMAS+PE groups (P = 0.146). Furthermore, the 28-days survival rates were significantly higher in DPMAS+PE group than that in PE group (57.4% vs 41.7%, P = 0.043) in the intermediate-advanced stage patients.
Conclusion: Compared with PE alone, DPMAS+PE might more effectively improve temporary TBIL in ACLF patients, and improve the 28-days survival rates in HBV-ACLF patients with intermediate-advanced stage. Therefore, DPMAS+PE may be an available ALSS treatment for HBV-ACLF patients.
Keywords: acute-on-chronic liver failure; artificial liver support; double plasma molecular absorption system; plasma exchange.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Apheresis published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic plasma exchange versus double plasma molecular absorption system in hepatitis B virus-infected acute-on-chronic liver failure treated by entercavir: A prospective study.J Clin Apher. 2017 Dec;32(6):453-461. doi: 10.1002/jca.21535. Epub 2017 Mar 17. J Clin Apher. 2017. PMID: 28304106
-
Comparison of plasma exchange, double plasma molecular adsorption system, and their combination in treating acute-on-chronic liver failure.J Int Med Res. 2020 Jun;48(6):300060520932053. doi: 10.1177/0300060520932053. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32552092 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and efficacy of double plasma molecular adsorption system with sequential low-volume plasma exchange in intermediate-stage hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure.J Med Virol. 2023 Mar;95(3):e28650. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28650. J Med Virol. 2023. PMID: 36897008 Clinical Trial.
-
Plasma exchange in patients with acute and acute-on-chronic liver failure: A systematic review.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Jan 14;26(2):219-245. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i2.219. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 31988586 Free PMC article.
-
The Clinical Efficacy of Double Plasma Molecular Absorption System Combined with Plasma Exchange in the Treatment of Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Mar 25;2022:3139929. doi: 10.1155/2022/3139929. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. PMID: 35368957 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
[Effect of artificial liver with double plasma molecular absorb system model on patients' platelets and corresponding treatment strategy].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Jun 18;54(3):548-551. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.03.022. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 35701134 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Mixed mode of artificial liver support in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure: a retrospective cohort study.Hepatol Int. 2023 Oct;17(5):1241-1250. doi: 10.1007/s12072-023-10573-2. Epub 2023 Aug 7. Hepatol Int. 2023. PMID: 37550499
-
Efficacy and Economic Evaluation of Nonbiological Artificial Liver Therapy in Acute-on-chronic Hepatitis B Liver Failure.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2023 Apr 28;11(2):433-440. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2022.00106. Epub 2022 Jul 1. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36643036 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Plasma Exchange in Certain Immune-Mediated Neurological Disorders: Focus on a Novel Nanomembrane-Based Technology.Biomedicines. 2023 Jan 25;11(2):328. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020328. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36830870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic plasma exchange in liver failure.World J Hepatol. 2021 Aug 27;13(8):904-915. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i8.904. World J Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34552697 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sarin SK, Kedarisetty CK, Abbas Z, et al. Acute‐on‐chronic liver failure: consensus recommendations of the Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver (APASL) 2014. Hepatol Int. 2014;8:453‐471. - PubMed
-
- Wu T, Li J, Shao L, et al. Development of diagnostic criteria and a prognostic score for hepatitis B virus‐related acute‐on‐chronic liver failure. Gut. 2017;67:2181‐2191. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ZYLX201806/Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals Clinical Medicine Development of Special Funding Support
- 2017YFA0103000/National Key R&D Program of China
- 2012ZX10002004-006/National Science and Technology Key Project on "Major Infectious Diseases such as HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis Prevention and Treatment"
- 2017ZX10203201-005/National Science and Technology Key Project on "Major Infectious Diseases such as HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis Prevention and Treatment"
- 2017ZX10201201/National Science and Technology Key Project on "Major Infectious Diseases such as HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis Prevention and Treatment"
- 2017ZX10202203-006-001/National Science and Technology Key Project on "Major Infectious Diseases such as HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis Prevention and Treatment"
- 2017ZX10302201-004-002/National Science and Technology Key Project on "Major Infectious Diseases such as HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis Prevention and Treatment"
- DFL20151601/"Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals" Ascent Plan
- Shanxi Province 136 Revitalization Medical Engineering
- 81600561/Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

