A systematic genetic screen identifies essential factors involved in nuclear size control
- PMID: 30759079
- PMCID: PMC6391033
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007929
A systematic genetic screen identifies essential factors involved in nuclear size control
Abstract
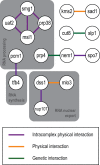
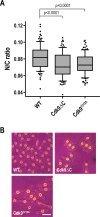
Nuclear size correlates with cell size, but the mechanism by which this scaling is achieved is not known. Here we screen fission yeast gene deletion mutants to identify essential factors involved in this process. Our screen has identified 25 essential factors that alter nuclear size, and our analysis has implicated RNA processing and LINC complexes in nuclear size control. This study has revealed lower and more extreme higher nuclear size phenotypes and has identified global cellular processes and specific structural nuclear components important for nuclear size control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
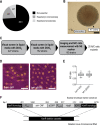
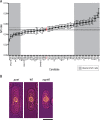
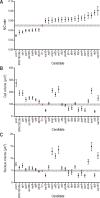
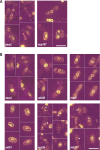
References
-
- Hertwig R. Ueber die Korrelation von Zell-und Kerngrösse und ihre Bedeutung für die Geschlechtliche Differenzierung und die Teilung der Zelle. Biologisches Centralblatt. 1903(23):4–62.
-
- Boveri T. Zellenstudien V. Über die Abhängigkeit der Kerngrösse und Zellenzahl bei Seeigellarven von der Chromosomenzahl der Ausganszellen. Jenaische Zeitschrift für Naturwissenschaft. 1905;39:445–524.
-
- Wilson EB. The Cell in Development and Heredity. 3 ed. New York: Macmillan; 1925.
-
- Gregory T. Genome size evolution in animals In: Gregory T, editor. The Evolution of the Genome. London: Elsevier Academic Press; 2005. p. 4–87.
-
- Conklin EG. Cell size and nuclear size. Journal of Experimental Zoology. 1912;12(1):1–98.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

