Late effects of total body irradiation on hematopoietic recovery and immune function in rhesus macaques
- PMID: 30759098
- PMCID: PMC6373904
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210663
Late effects of total body irradiation on hematopoietic recovery and immune function in rhesus macaques
Abstract
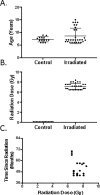
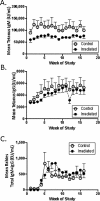
While exposure to radiation can be lifesaving in certain settings, it can also potentially result in long-lasting adverse effects, particularly to hematopoietic and immune cells. This study investigated hematopoietic recovery and immune function in rhesus macaques Cross-sectionally (at a single time point) 2 to 5 years after exposure to a single large dose (6.5 to 8.4 Gray) of total body radiation (TBI) derived from linear accelerator-derived photons (2 MeV, 80 cGy/minute) or Cobalt 60-derived gamma irradiation (60 cGy/min). Hematopoietic recovery was assessed through measurement of complete blood counts, lymphocyte subpopulation analysis, and thymus function assessment. Capacity to mount specific antibody responses against rabies, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and tetanus antigens was determined 2 years after TBI. Irradiated macaques showed increased white blood cells, decreased platelets, and decreased frequencies of peripheral blood T cells. Effects of prior radiation on production and export of new T cells by the thymus was dependent on age at the time of analysis, with evidence of interaction with radiation dose for CD8+ T cells. Irradiated and control animals mounted similar mean antibody responses to proteins from tetanus and rabies and to 10 of 11 serotype-specific pneumococcal polysaccharides. However, irradiated animals uniformly failed to make antibodies against polysaccharides from serotype 5 pneumococci, in contrast to the robust responses of non-irradiated controls. Trends toward decreased serum levels of anti-tetanus IgM and slower peak antibody responses to rabies were also observed. Taken together, these data show that dose-related changes in peripheral blood cells and immune responses to both novel and recall antigens can be detected 2 to 5 years after exposure to whole body radiation. Longer term follow-up data on this cohort and independent validation will be helpful to determine whether these changes persist or whether additional changes become evident with increasing time since radiation, particularly as animals begin to develop aging-related changes in immune function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Kong F, Chen CH, Cooper MD. Thymic function can be accurately monitored by the level of recent T cell emigrants in the circulation. Immunity. 1998;8: 97–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

