The Association of Antibiotic Stewardship With Fluoroquinolone Prescribing in Michigan Hospitals: A Multi-hospital Cohort Study
- PMID: 30759198
- PMCID: PMC6763628
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciy1102
The Association of Antibiotic Stewardship With Fluoroquinolone Prescribing in Michigan Hospitals: A Multi-hospital Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: Fluoroquinolones increase the risk of Clostridioides difficile infection and antibiotic resistance. Hospitals often use pre-prescription approval or prospective audit and feedback to target fluoroquinolone prescribing. Whether these strategies impact aggregate fluoroquinolone use is unknown.
Methods: This study is a 48-hospital, retrospective cohort of general-care, medical patients hospitalized with pneumonia or positive urine culture between December 2015-September 2017. Hospitals were surveyed on their use of pre-prescription approval and/or prospective audit and feedback to target fluoroquinolone prescribing during hospitalization (fluoroquinolone stewardship). After controlling for hospital clustering and patient factors, aggregate (inpatient and post-discharge) fluoroquinolone (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin) exposure was compared between hospitals with and without fluoroquinolone stewardship.
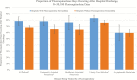
Results: There were 11 748 patients (6820 pneumonia; 4928 positive urine culture) included at 48 hospitals. All hospitals responded to the survey: 29.2% (14/48) reported using pre-prescription approval and/or prospective audit and feedback to target fluoroquinolone prescribing. After adjustment, fluoroquinolone stewardship was associated with fewer patients receiving a fluoroquinolone (37.1% vs 48.2%; P = .01) and fewer fluoroquinolone treatment days per 1000 patients (2282 vs 3096 days/1000 patients; P = .01), driven by lower inpatient prescribing. However, most (66.6%) fluoroquinolone treatment days occurred after discharge, and hospitals with fluoroquinolone stewardship had twice as many new fluoroquinolone starts after discharge as hospitals without (15.6% vs 8.4%; P = .003).
Conclusions: Hospital-based stewardship interventions targeting fluoroquinolone prescribing were associated with less fluoroquinolone prescribing during hospitalization, but not at discharge. To limit aggregate fluoroquinolone exposure, stewardship programs should target both inpatient and discharge prescribing.
Keywords: antibiotic stewardship; fluoroquinolone; pneumonia; transitions of care; urinary tract infection.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures
Comment in
-
Oral Antibiotic Prescribing in Healthcare-associated Pneumonia Patients at Hospital Discharge.Clin Infect Dis. 2019 Nov 13;69(11):2042-2043. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz340. Clin Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31211833 No abstract available.
-
Reply to Truong, Hsu, and Yamaki.Clin Infect Dis. 2019 Nov 13;69(11):2043-2044. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz342. Clin Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31211840 No abstract available.
References
-
- Pépin J, Saheb N, Coulombe MA, et al. . Emergence of fluoroquinolones as the predominant risk factor for Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea: a cohort study during an epidemic in Quebec. Clin Infect Dis 2005; 41:1254–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical