Advanced Hepatitis C Virus Replication PDE Models within a Realistic Intracellular Geometric Environment
- PMID: 30759770
- PMCID: PMC6388173
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph16030513
Advanced Hepatitis C Virus Replication PDE Models within a Realistic Intracellular Geometric Environment
Abstract
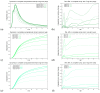
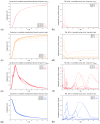
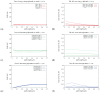
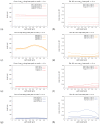
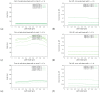
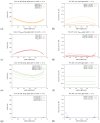
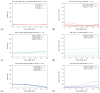
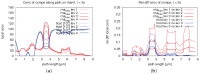
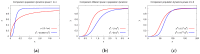
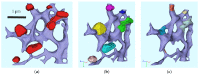
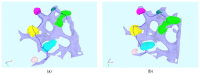
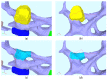
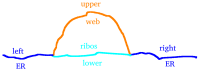
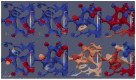
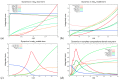
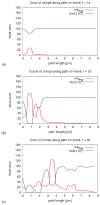
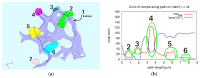
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA replication cycle is a dynamic intracellular process occurring in three-dimensional space (3D), which is difficult both to capture experimentally and to visualize conceptually. HCV-generated replication factories are housed within virus-induced intracellular structures termed membranous webs (MW), which are derived from the Endoplasmatic Reticulum (ER). Recently, we published 3D spatiotemporal resolved diffusion⁻reaction models of the HCV RNA replication cycle by means of surface partial differential equation (sPDE) descriptions. We distinguished between the basic components of the HCV RNA replication cycle, namely HCV RNA, non-structural viral proteins (NSPs), and a host factor. In particular, we evaluated the sPDE models upon realistic reconstructed intracellular compartments (ER/MW). In this paper, we propose a significant extension of the model based upon two additional parameters: different aggregate states of HCV RNA and NSPs, and population dynamics inspired diffusion and reaction coefficients instead of multilinear ones. The combination of both aspects enables realistic modeling of viral replication at all scales. Specifically, we describe a replication complex state consisting of HCV RNA together with a defined amount of NSPs. As a result of the combination of spatial resolution and different aggregate states, the new model mimics a cis requirement for HCV RNA replication. We used heuristic parameters for our simulations, which were run only on a subsection of the ER. Nevertheless, this was sufficient to allow the fitting of core aspects of virus reproduction, at least qualitatively. Our findings should help stimulate new model approaches and experimental directions for virology.
Keywords: (surface) partial differential equations; 3D spatiotemporal resolved mathematical models; Finite Volumes; computational virology; hepatitis C virus (HCV); massively parallel multigrid solvers; mathematical models of viral RNA cycle; population dynamics; realistic geometries; viral dynamics; within-host viral modeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
-
- Romero-Brey I., Merz A., Chiramel A., Lee J., Chlanda P., Haselman U., Santarella-Mellwig R., Habermann A., Hoppe S., Kallis S., et al. Three-dimensional architecture and biogenesis of membrane structures associated with hepatitis C virus replication. PLoS Path. 2012;8:e1003056. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003056. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

