Engineering of Fatty Acid Synthases (FASs) to Boost the Production of Medium-Chain Fatty Acids (MCFAs) in Mucor circinelloides
- PMID: 30759801
- PMCID: PMC6387429
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20030786
Engineering of Fatty Acid Synthases (FASs) to Boost the Production of Medium-Chain Fatty Acids (MCFAs) in Mucor circinelloides
Abstract
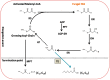
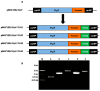
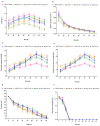
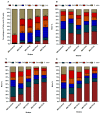
Increasing energy demands and health-related concerns worldwide have motivated researchers to adopt diverse strategies to improve medium-chain fatty acid (MCFA) biosynthesis for use in the functional food and aviation industries. The abundance of naturally produced MCFAs from botanical sources (i.e., coconut fruit/seeds and palm tree) has been observed to be insufficient compared with the various microorganisms used to cope with industrial demands. Mucor circinelloides is one of many promising microorganisms; it exhibits diverse biotechnological importance ranging from the production of functional lipids to applications in the manufacture of bio-fuel. Thus, research was conducted to acquire the desired elevated amounts of MCFAs (i.e., C8⁻C12) from metabolically engineered strains of M. circinelloides M65. To achieve this goal, four different acyl-acyl carrier protein (ACP) thioesterase (TE)-encoding genes exhibiting a substrate preference for medium-chain acyl-ACP molecules were expressed in M. circinelloides M65, resulting in the generation of C8⁻C12 fatty acids. Among all the engineered strains, M65-TE-03 and M65-TE-04 demonstrated the highest production of non-native C8⁻C10 and C12 fatty acids, respectively, in comparison to the control. These recombinant strains biosynthesized MCFAs de novo within the range from 28 to 46% (i.e., 1.14 to 2.77 g/L) of total cell lipids. Moreover, the reduction in chain length eventually resulted in a 1.5⁻1.75-fold increase in total lipid productivity in the engineered strains. The MCFAs were also found to be integrated into all lipid classes. This work illustrates how the integration of heterologous enzymes in M. circinelloides can offer a novel opportunity to edit the fatty acid synthases (FAS) complex, resulting in increased production of microbial MFCAs.
Keywords: Mucor circinelloides; bio-fuels; medium-chain fatty acids; metabolic engineering; microbial lipids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased Accumulation of Medium-Chain Fatty Acids by Dynamic Degradation of Long-Chain Fatty Acids in Mucor circinelloides.Genes (Basel). 2020 Aug 5;11(8):890. doi: 10.3390/genes11080890. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32764225 Free PMC article.
-
Matching Protein Interfaces for Improved Medium-Chain Fatty Acid Production.ACS Synth Biol. 2018 May 18;7(5):1179-1187. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.7b00334. Epub 2018 May 3. ACS Synth Biol. 2018. PMID: 29722970 Free PMC article.
-
Mucor circinelloides: a model organism for oleaginous fungi and its potential applications in bioactive lipid production.Microb Cell Fact. 2022 Feb 28;21(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12934-022-01758-9. Microb Cell Fact. 2022. PMID: 35227264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A mass spectrometry-based high-throughput screening method for engineering fatty acid synthases with improved production of medium-chain fatty acids.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2020 Jul;117(7):2131-2138. doi: 10.1002/bit.27343. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2020. PMID: 32219854
-
Advancing oleaginous microorganisms to produce lipid via metabolic engineering technology.Prog Lipid Res. 2013 Oct;52(4):395-408. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.05.002. Epub 2013 May 16. Prog Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23685199 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances in metabolic engineering of microorganisms for advancing lignocellulose-derived biofuels.Bioengineered. 2022 Apr;13(4):8135-8163. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2051856. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35297313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and Functional Characterization of Adenosine Deaminase in Mucor circinelloides: A Novel Potential Regulator of Nitrogen Utilization and Lipid Biosynthesis.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Jul 26;8(8):774. doi: 10.3390/jof8080774. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35893142 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Accumulation of Medium-Chain Fatty Acids by Dynamic Degradation of Long-Chain Fatty Acids in Mucor circinelloides.Genes (Basel). 2020 Aug 5;11(8):890. doi: 10.3390/genes11080890. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32764225 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of the Mitochondrial Malic Enzyme Genes (malC and malD) Improved the Lipid Accumulation in Mucor circinelloides WJ11.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jun 22;13:919364. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.919364. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35814694 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Modification of Mucor circinelloides to Construct Stearidonic Acid Producing Cell Factory.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 4;20(7):1683. doi: 10.3390/ijms20071683. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30987311 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Knothe G. “Designer” biodiesel: Optimizing fatty ester composition to improve fuel properties. Energy Fuels. 2008;22:1358–1364. doi: 10.1021/ef700639e. - DOI
-
- Chang Y.W., Lee D., Bae S.Y. Preparation of polyethylene-octene elastomer/clay nanocomposite and microcellular foam processed in supercritical carbon dioxide. Polym. Int. 2006;55:184–189. doi: 10.1002/pi.1936. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

