Characterization and Source Identification of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs) in Air in Xi'an: Based on a Five-Year Study
- PMID: 30759827
- PMCID: PMC6388259
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph16030520
Characterization and Source Identification of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs) in Air in Xi'an: Based on a Five-Year Study
Abstract
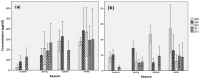
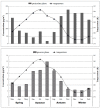
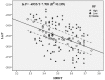
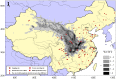
In order to assess polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) atmospheric pollution levels in Xi'an, air samples were collected using a large flow air sampler from July 2008 to April 2013. In total, 134 samples were collected and 12 PBDE congeners were detected. Total PBDE concentrations (both gaseous and particulate phase) were 36.38⁻1054 pg/m³, with an average of 253.2 ± 198.4 pg/m³. BDE-209 was identified as the main PBDE component, with a corresponding concentration of 0.00⁻1041 pg/m³, accounting for 89.4% of total PBDEs. Principal component analysis results showed that PBDEs in Xi'an's atmosphere mainly originated from commercial products containing penta-BDE, octa-BDE, and deca-BDE. The relative natural logarithm for partial pressure (RP) of PBDEs (gaseous phase) was calculated using the Clausius⁻Clapeyron equation. The gas flow trajectories at high, middle, and low RP values were analyzed by applying the backward trajectory model. These data indicated that the difference between trajectory distribution and concentration load on trajectories was huge under different RP values. PBDE concentrations (gaseous phase) weighted trajectory showed that the central and southwestern parts of Henan Province and the northwestern area of Hubei Province exhibited the darkest colors, and the daily average concentration contribution of PBDEs to the receiving point was >9 pg/m³, which indicates that these areas might be the main potential source areas of PBDEs in Xi'an's atmosphere.
Keywords: CWT; Xi’an; atmosphere; backward trajectory; polybrominated diphenyl ethers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mehran A., Pedro A., Andreas S.D., Ake B. An overview of commercially used brominated flame retardants, their applications, their use patterns in different countries/regions and possible modes of release. Environ. Int. 2004;29:683–689. - PubMed
-
- Andersson Ö., Blomkvist G. Polybrominated aromatic pollutants found in fish in Sweden. Chemosphere. 1981;10:1051–1060. doi: 10.1016/0045-6535(81)90216-2. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

