Korean Thistle (Cirsium japonicum var. maackii (Maxim.) Matsum.): A Potential Dietary Supplement against Diabetes and Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 30759846
- PMCID: PMC6385118
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24030649
Korean Thistle (Cirsium japonicum var. maackii (Maxim.) Matsum.): A Potential Dietary Supplement against Diabetes and Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
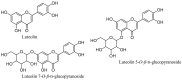
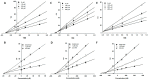
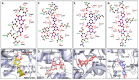
In the search for natural products having a dual inhibitory action on diabetes and Alzheimer's disease, this study investigated the activity of different parts of Korean thistle (Cirsium japonicum var. maackii (Maxim.) Matsum), and its fractional constituents by in vitro enzymatic and in silico molecular docking studies. Cirsium maackii has been used as a traditional medicine for the treatment of several diseases. The ethyl acetate and dichloromethane fractions of a leaf extract showed α-glucosidase and BACE1 inhibitory activity, respectively. Furthermore, the isolated compound, luteolin, exhibited concentration-dependent non-competitive inhibition against both α-glucosidase and BACE1 (IC50 = 51.27 ± 1.23 and 13.75 ± 0.26 μM; Ki value = 52.04 and 14.76 μM, respectively). Moreover, docking studies showed that luteolin formed a strong hydrogen bond with the peripheral binding amino acid residues, and hydrophobic interactions with the α-glucosidase and BACE1 enzymes. Therefore, Korean thistle may act as an important dietary supplement against diabetes and Alzheimer's disease, especially the leaves, because of the preponderance of the active component, luteolin, making Korean thistle a promising candidate for more detailed in vitro and in vivo studies.
Keywords: BACE1; Cirsium maackii; Korean thistle; luteolin; supplements; α-Glucosidase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

