Novel Antiplatelet Therapies for Atherothrombotic Diseases
- PMID: 30760019
- PMCID: PMC6445601
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.310955
Novel Antiplatelet Therapies for Atherothrombotic Diseases
Abstract
Antiplatelet therapies are an essential tool to reduce the risk of developing clinically apparent atherothrombotic disease and are a mainstay in the therapy of patients who have established cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, and peripheral artery disease. Strategies to intensify antiplatelet regimens are limited by concomitant increases in clinically significant bleeding. The development of novel antiplatelet therapies targeting additional receptor and signaling pathways, with a focus on maintaining antiplatelet efficacy while preserving hemostasis, holds tremendous potential to improve outcomes among patients with atherothrombotic diseases.
Keywords: acute coronary syndrome; cardiovascular disease; hemostasis; myocardial infarction; thrombosis.
Figures
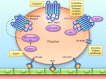

References
-
- Herrington W, Lacey B, Sherliker P, Armitage J, Lewington S. Epidemiology of atherosclerosis and the potential to reduce the global burden of atherothrombotic disease. Circ Res. 2016;118:535–546. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.307611. - PubMed
-
- Bowman L, Mafham M, Wallendszus K, et al. ASCEND Study Collaborative Group. Effects of aspirin for primary prevention in persons with diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:1529–1539. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1804988. - PubMed
-
- Gaziano JM, Brotons C, Coppolecchia R, Cricelli C, Darius H, Gorelick PB, Howard G, Pearson TA, Rothwell PM, Ruilope LM, Tendera M, Tognoni G ARRIVE Executive Committee. Use of aspirin to reduce risk of initial vascular events in patients at moderate risk of cardiovascular disease (ARRIVE): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;392:1036–1046. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31924-X. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

