Time resolved gene expression analysis during tamoxifen adaption of MCF-7 cells identifies long non-coding RNAs with prognostic impact
- PMID: 30760083
- PMCID: PMC6546408
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2019.1581597
Time resolved gene expression analysis during tamoxifen adaption of MCF-7 cells identifies long non-coding RNAs with prognostic impact
Abstract
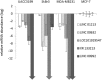
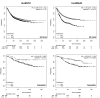
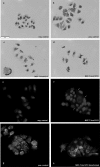
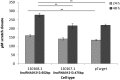
Acquired tamoxifen resistance is a persistent problem for the treatment of estrogen receptor positive, premenopausal breast cancer patients and predictive biomarkers are still elusive. We here analyzed gene expression changes in a cellular model to identify early and late changes upon tamoxifen exposure and thereby novel prognostic biomarkers. Estrogen receptor positive MCF-7 cells were incubated with 4OH-tamoxifen (10 nM) and gene expression analyzed by array hybridization during 12 weeks. Array results were confirmed by nCounter- and qRT-PCR technique. Pathway enrichment analysis revealed that early responses concerned mainly amine synthesis and NRF2-related signaling and evolved into a stable gene expression pattern within 4 weeks characterized by changes in glucuronidation-, estrogen metabolism-, nuclear receptor- and interferon signaling pathways. As a large number of long non coding RNAs was subject to regulation, we investigated 5 of these (linc01213, linc00632 linc0992, LOC101929547 and XR_133213) in more detail. From these, only linc01213 was upregulated but all were less abundant in estrogen-receptor negative cell lines (MDA-MB 231, SKBR-3 and UACC3199). In a web-based survival analysis linc01213 and linc00632 turned out to have prognostic impact. Linc01213 was investigated further by plasmid-mediated over-expression as well as siRNA down-regulation in MCF-7 cells. Nevertheless, this had no effect on proliferation or expression of tamoxifen regulated genes, but migration was increased. In conclusion, the cellular model identified a set of lincRNAs with prognostic relevance for breast cancer. One of these, linc01213 although regulated by 4OH-tamoxifen, is not a central regulator of tamoxifen adaption, but interferes with the regulation of migration.
Keywords: Breast cancer; biomarker; gene expression; long-non coding RNAs; tamoxifen.
Figures
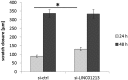
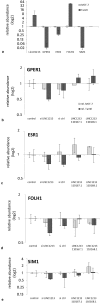
References
-
- Servick K. Breast cancer: a world of differences. Science. 2014;343:1452–1453. - PubMed
-
- Rakha EA, Green AR. Molecular classification of breast cancer: what the pathologist needs to know. Pathology. 2017;49:111–119. - PubMed
-
- Chia SK, Wolff AC. With maturity comes confidence: EBCTCG tamoxifen update. Lancet. 2011;378:747–749. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
