An essential role for α4A-tubulin in platelet biogenesis
- PMID: 30760556
- PMCID: PMC6374996
- DOI: 10.26508/lsa.201900309
An essential role for α4A-tubulin in platelet biogenesis
Erratum in
-
Correction: An essential role for α4A-tubulin in platelet biogenesis.Life Sci Alliance. 2021 Jun 21;4(8):e202101132. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202101132. Print 2021 Aug. Life Sci Alliance. 2021. PMID: 34155037 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
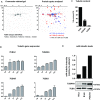
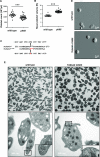
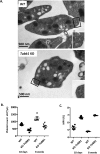
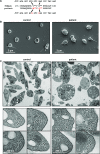
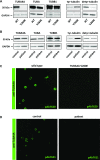
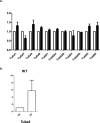
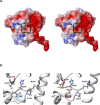
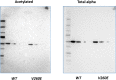
During platelet biogenesis, microtubules (MTs) are arranged into submembranous structures (the marginal band) that encircle the cell in a single plane. This unique MT array has no equivalent in any other mammalian cell, and the mechanisms responsible for this particular mode of assembly are not fully understood. One possibility is that platelet MTs are composed of a particular set of tubulin isotypes that carry specific posttranslational modifications. Although β1-tubulin is known to be essential, no equivalent roles of α-tubulin isotypes in platelet formation or function have so far been reported. Here, we identify α4A-tubulin as a predominant α-tubulin isotype in platelets. Similar to β1-tubulin, α4A-tubulin expression is up-regulated during the late stages of megakaryocyte differentiation. Missense mutations in the α4A-tubulin gene cause macrothrombocytopenia in mice and humans. Defects in α4A-tubulin lead to changes in tubulin tyrosination status of the platelet tubulin pool. Ultrastructural defects include reduced numbers and misarranged MT coils in the platelet marginal band. We further observed defects in megakaryocyte maturation and proplatelet formation in Tuba4a-mutant mice. We have, thus, discovered an α-tubulin isotype with specific and essential roles in platelet biogenesis.
© 2019 Strassel et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kenney DM, Linck RW (1985) The cystoskeleton of unstimulated blood platelets: Structure and composition of the isolated marginal microtubular band. J Cell Sci 78: 1–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
