Sleep modulates haematopoiesis and protects against atherosclerosis
- PMID: 30760925
- PMCID: PMC6442744
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-0948-2
Sleep modulates haematopoiesis and protects against atherosclerosis
Abstract
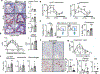
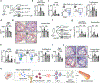
Sleep is integral to life1. Although insufficient or disrupted sleep increases the risk of multiple pathological conditions, including cardiovascular disease2, we know little about the cellular and molecular mechanisms by which sleep maintains cardiovascular health. Here we report that sleep regulates haematopoiesis and protects against atherosclerosis in mice. We show that mice subjected to sleep fragmentation produce more Ly-6Chigh monocytes, develop larger atherosclerotic lesions and produce less hypocretin-a stimulatory and wake-promoting neuropeptide-in the lateral hypothalamus. Hypocretin controls myelopoiesis by restricting the production of CSF1 by hypocretin-receptor-expressing pre-neutrophils in the bone marrow. Whereas hypocretin-null and haematopoietic hypocretin-receptor-null mice develop monocytosis and accelerated atherosclerosis, sleep-fragmented mice with either haematopoietic CSF1 deficiency or hypocretin supplementation have reduced numbers of circulating monocytes and smaller atherosclerotic lesions. Together, these results identify a neuro-immune axis that links sleep to haematopoiesis and atherosclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Financial Interests
None.
Figures

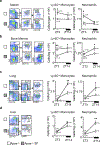

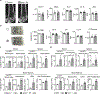
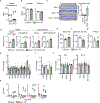




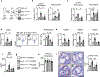
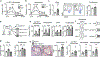

Comment in
-
How broken sleep promotes cardiovascular disease.Nature. 2019 Feb;566(7744):329-330. doi: 10.1038/d41586-019-00393-6. Nature. 2019. PMID: 30783270 No abstract available.
-
Sleep reduces haematopoiesis and atherosclerosis via a neuroimmune axis.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2019 Apr;16(4):199. doi: 10.1038/s41569-019-0174-5. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30804495 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cappuccio FP, Cooper D, D’Elia L, Strazzullo P & Miller MA Sleep duration predicts cardiovascular outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Eur Heart J 32, 1484–1492 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

