p31-43 Gliadin Peptide Forms Oligomers and Induces NLRP3 Inflammasome/Caspase 1- Dependent Mucosal Damage in Small Intestine
- PMID: 30761127
- PMCID: PMC6363691
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00031
p31-43 Gliadin Peptide Forms Oligomers and Induces NLRP3 Inflammasome/Caspase 1- Dependent Mucosal Damage in Small Intestine
Abstract
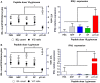
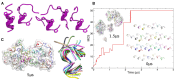
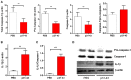
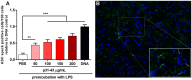
Celiac disease (CD) is a chronic enteropathy elicited by a Th1 response to gluten peptides in the small intestine of genetically susceptible individuals. However, it remains unclear what drives the induction of inflammatory responses of this kind against harmless antigens in food. In a recent work, we have shown that the p31-43 peptide (p31-43) from α-gliadin can induce an innate immune response in the intestine and that this may initiate pathological adaptive immunity. The receptors and mechanisms responsible for the induction of innate immunity by p31-43 are unknown and here we present evidence that this may reflect conformational changes in the peptide that allow it to activate the NLRP3 inflammasome. Administration of p31-43, but not scrambled or inverted peptides, to normal mice induced enteropathy in the proximal small intestine, associated with increased production of type I interferon and mature IL-1β. P31-43 showed a sequence-specific spontaneous ability to form structured oligomers and aggregates in vitro and induced activation of the ASC speck complex. In parallel, the enteropathy induced by p31-43 in vivo did not occur in the absence of NLRP3 or caspase 1 and was inhibited by administration of the caspase 1 inhibitor Ac-YVAD-cmk. Collectively, these findings show that p31-43 gliadin has an intrinsic propensity to form oligomers which trigger the NLRP3 inflammasome and that this pathway is required for intestinal inflammation and pathology when p31-43 is administered orally to mice. This innate activation of the inflammasome may have important implications in the initial stages of CD pathogenesis.
Keywords: caspase-1; celiac disease; enteropathy; gliadin peptides; inflammasome; innate immunity; p31-43; small intestine damage.
Figures




Comment in
-
Commentary: p31-43 Gliadin Peptide Forms Oligomers and Induces NLRP3 Inflammasome/Caspase 1- Dependent Mucosal Damage in Small Intestine.Front Immunol. 2019 Nov 29;10:2792. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02792. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31849971 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

