Regulation of Type 2 Immunity in Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 30761134
- PMCID: PMC6362944
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00062
Regulation of Type 2 Immunity in Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
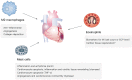
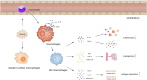
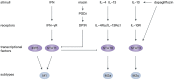
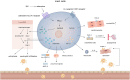
Type 2 immunity participates in the pathogeneses of helminth infection and allergic diseases. Emerging evidence indicates that the components of type 2 immunity are also involved in maintaining metabolic hemostasis and facilitating the healing process after tissue injury. Numerous preclinical studies have suggested regulation of type 2 immunity-related cytokines, such as interleukin-4, -13, and -33, and cell types, such as M2 macrophages, mast cells, and eosinophils, affects cardiac functions after myocardial infarction (MI), providing new insights into the importance of immune modulation in the infarcted heart. This review provides an overview of the functions of these cytokines and cells in the setting of MI as well as their potential to predict the severity and prognosis of MI.
Keywords: M2 macrophages; eosinophils; immune modulation; interleukin; mast cells; myocardial infarction; type 2 immunity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of Neutrophils in Cardiac Injury and Repair Following Myocardial Infarction.Cells. 2021 Jul 2;10(7):1676. doi: 10.3390/cells10071676. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34359844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of interleukin-6 in regulation of immune responses to remodeling after myocardial infarction.Heart Fail Rev. 2015 Jan;20(1):25-38. doi: 10.1007/s10741-014-9431-1. Heart Fail Rev. 2015. PMID: 24756455 Review.
-
Cardiac CD68+ and stabilin-1+ macrophages in wound healing following myocardial infarction: From experiment to clinic.Immunobiology. 2018 Apr-May;223(4-5):413-421. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2017.11.006. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Immunobiology. 2018. PMID: 29179985
-
The Innate Immune Response in Myocardial Infarction, Repair, and Regeneration.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1003:251-272. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-57613-8_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28667562 Review.
-
Loss of Macrophage Wnt Secretion Improves Remodeling and Function After Myocardial Infarction in Mice.J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 Jan 6;6(1):e004387. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.004387. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017. PMID: 28062479 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Recent Progress in Advanced Polyester Elastomers for Tissue Engineering and Bioelectronics.Molecules. 2023 Dec 9;28(24):8025. doi: 10.3390/molecules28248025. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38138515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of the differences in immune-related genes and immune cell subtypes in acute myocardial infarction.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2024 Oct 14;57:e14345. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2024e14345. eCollection 2024. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2024. PMID: 39417451 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophils improve cardiac function after myocardial infarction.Nat Commun. 2020 Dec 16;11(1):6396. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19297-5. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33328477 Free PMC article.
-
Novel diagnostic biomarkers related to necroptosis and immune infiltration landscape in acute myocardial infarction.PeerJ. 2024 Feb 26;12:e17044. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17044. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38426147 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Immune-Related Genes in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction Using Machine Learning Methods.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Jun 3;15:3305-3321. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S360498. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35692951 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Szkodzinski J, Hudzik B, Osuch M, Romanowski W, Szygula-Jurkiewicz B, Polonski L, et al. . Serum concentrations of interleukin-4 and interferon-gamma in relation to severe left ventricular dysfunction in patients with acute myocardial infarction undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Heart Vessels (2011) 26:399–407. 10.1007/s00380-010-0076-2 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

