New biomarkers of Kawasaki disease identified by urine proteomic analysis
- PMID: 30761252
- PMCID: PMC6356163
- DOI: 10.1002/2211-5463.12563
New biomarkers of Kawasaki disease identified by urine proteomic analysis
Abstract
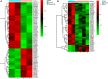
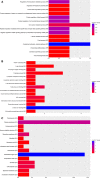
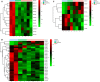
Kawasaki disease (KD) is an acute systemic vasculitis that mainly afflicts infants and young children. The symptoms of KD are similar to those of various febrile diseases. Here, we attempted to develop accurate diagnostic biomarkers of KD by performing urine proteomic analysis of samples from healthy controls, patients with KD, and patients with another febrile disease, pneumonia (two patients). We identified differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) in KD as compared to normal controls. We also constructed functional annotation and protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks of DEPs in KD and pneumonia. DEPs common to both KD and pneumonia were identified, as well as DEPs specific to KD. Compared to normal control, 43 and 62 DEPs were identified in KD and pneumonia, respectively. Serine hydroxymethyltransferase 1 is a hub protein of the KD-specific PPI network. Thirteen DEPs common to both KD and pneumonia and 30 DEPs specific to KD were identified. Of these, the expression of eight DEPs could cluster normal and pneumonia samples into one group and cluster KD samples into another group based on hierarchical clustering. Our study identified several DEPs that may play a role in KD and that may serve as diagnostic biomarkers to distinguish patients with KD from both normal control and other febrile diseases.
Keywords: Kawasaki disease; biomarker; pneumonia; protein; urine proteomics.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Plasma Exosomal-Derived SERPINA1 and GNAI2 Downregulation as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers of Kawasaki Disease with Coronary Artery Aneurysms.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 16;26(6):2668. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062668. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141310 Free PMC article.
-
[Proteomics of serum exosomes in children in the acute stage of Kawasaki disease: a prospective study].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2022 Apr 15;24(4):392-398. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2110110. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35527414 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Urine proteomics for discovery of improved diagnostic markers of Kawasaki disease.EMBO Mol Med. 2013 Feb;5(2):210-20. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201201494. Epub 2012 Dec 20. EMBO Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23281308 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics approach for biomarker discovery in Kawasaki disease.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2024 Dec;20(12):1449-1460. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2024.2383236. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39041312 Review.
-
Upcoming biomarkers for the diagnosis of Kawasaki disease: A review.Clin Biochem. 2015 Nov;48(16-17):1188-94. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2015.02.013. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Clin Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25749557 Review.
Cited by
-
[Quantitative proteomics and bioinformatics analyses of human coronary artery endothelial cell injury induced by Kawasaki disease].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Jul;22(7):796-803. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2001069. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32669181 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Metabolic profiling reveals altered tryptophan metabolism in patients with kawasaki disease.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 May 4;10:1180537. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1180537. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37214338 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Exosomal-Derived SERPINA1 and GNAI2 Downregulation as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers of Kawasaki Disease with Coronary Artery Aneurysms.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 16;26(6):2668. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062668. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141310 Free PMC article.
-
New biomarkers of Kawasaki disease identified by gingival crevicular fluid proteomics.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 May 12;12:1597412. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1597412. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40421421 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Gerber MA, Gewitz MH, Tani LY, Burns JC, Shulman ST, Bolger AF, Ferrieri P, Baltimore RS et al (2004) Diagnosis, treatment, and long‐term management of Kawasaki disease: a statement for health professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Pediatrics 114, 1708–1733. - PubMed
-
- No SJ, Kim DO, Choi KM and Eun LY (2013) Do predictors of incomplete Kawasaki disease exist for infants? Pediatr Cardiol 34, 286–290. - PubMed
-
- Ng YM, Sung RY, So LY, Fong NC, Ho MH, Cheng YW, Lee SH, Mak WC, Wong DM, Yam MC et al (2005) Kawasaki disease in Hong Kong, 1994 to 2000. Hong Kong Med J 11, 331–335. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

