Severe Refractory Paraneoplastic Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid Successfully Treated With Rituximab
- PMID: 30761304
- PMCID: PMC6362419
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2019.00008
Severe Refractory Paraneoplastic Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid Successfully Treated With Rituximab
Abstract
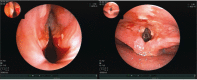
Mucous membrane pemphigoid (MMP) is a rare autoimmune bullous disease of the mucous membranes, which can cause irreversible scarring and is discussed to be associated with cancer, if laminin-332-autoantibodies are present. MMP with severe ocular and laryngeal involvement is difficult to treat and can be treatment-refractory to conventional immunosuppressant therapy. A 67-year-old man with a history of prostate cancer presented to our clinic with sore throat, intraoral bullae, odynophagia, dysphonia, exertional dyspnea, and erosions of the glans penis. Clinical examination confirmed a laryngo-pharyngitis with involvement of the epiglottis and bilateral symblepharon. Diagnostics comprising multiple biopsies, direct and indirect immunofluorescence, serology analysis, and immunoblotting confirmed the diagnosis of a paraneoplastic MMP by showing a subepithelial split in histology and the presence of anti-laminin-332-antibodies. Despite combined systemic treatment with prednisolone and either dapsone or azathioprine, a progress of the disease occurred leading to severe ocular and laryngeal complications. Two month after rituximab treatment, complete disease control was achieved. This case report shows a severe ocular and life threatening laryngeal involvement of therapy-refractory paraneoplastic MMP highlighting the importance of interdisciplinary management and difficulty of diagnosing MMP despite repeated diagnostic testing.
Keywords: laminin 332; mucous membrane pemphigoid; paraneoplastic; rituxmab; therapy refractoriness.
Figures



References
-
- Chan LS, Ahmed AR, Anhalt GJ, Bernauer W, Cooper KD, Elder MJ, et al. The first international consensus on mucous membrane pemphigoid: definition, diagnostic criteria, pathogenic factors, medical treatment, and prognostic indicators. Arch Dermatol. (2002) 138:370–9. 10.1001/archderm.138.3.370 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

