Post-hepatectomy liver regeneration in the context of bile acid homeostasis and the gut-liver signaling axis
- PMID: 30761355
- PMCID: PMC6370335
- DOI: 10.18053/jctres.04.201801.001
Post-hepatectomy liver regeneration in the context of bile acid homeostasis and the gut-liver signaling axis
Abstract
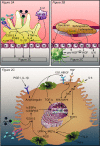
Background: Liver regeneration following partial hepatectomy (PHx) is a complicated process involving multiple organs and several types of signaling networks. The bile acid-activated metabolic pathways occupy an auxiliary yet important chapter in the entire biochemical story. PHx is characterized by rapid but transient bile acid overload in the liver, which constitutes the first wave of proliferative signaling in the remnant hepatocytes. Bile acids trigger hepatocyte proliferation through activation of several nuclear receptors. Following biliary passage into the intestines, enterocytes reabsorb the bile acids, which results in the activation of farnesoid X receptor (FXR), the consequent excretion of fibroblast growth factor (FGF)19/FGF15, and its release into the enterohepatic circulation. FGF19/FGF15 subsequently binds to its cognate receptor, fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4) complexed with β-klotho, on the hepatocyte membrane, which initiates the second wave of proliferative signaling. Because some bile acids are toxic, the remnant hepatocytes must resolve the potentially detrimental state of bile acid excess. Therefore, the hepatocytes orchestrate a bile acid detoxification and elimination response as a protective mechanism in concurrence with the proliferative signaling. The response in part results in the excretion of (biotransformed) bile acids into the canalicular system, causing the bile acids to end up in the intestines.
Relevance for patients: Recently, FXR agonists have been shown to promote regeneration via the gut-liver axis. This type of pharmacological intervention may prove beneficial for patients with hepatobiliary tumors undergoing PHx. In light of these developments, the review provides an in-depth account of the pathways that underlie post-PHx liver regeneration in the context of bile acid homeostasis in the liver and the gut-liver signaling axis.
Keywords: arnesoid X receptor enteral; detoxification; fibroblast growth factor; hepatocyte proliferation; mitotic signaling; surgery; transport and canalicular excretion.
Figures












Similar articles
-
Unaltered Liver Regeneration in Post-Cholestatic Rats Treated with the FXR Agonist Obeticholic Acid.Biomolecules. 2021 Feb 10;11(2):260. doi: 10.3390/biom11020260. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33578971 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor 15 deficiency impairs liver regeneration in mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014 May 15;306(10):G893-902. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00337.2013. Epub 2014 Apr 3. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24699334 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte-specific deletion of farnesoid X receptor delays but does not inhibit liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in mice.Hepatology. 2012 Dec;56(6):2344-52. doi: 10.1002/hep.25918. Hepatology. 2012. PMID: 22730081 Free PMC article.
-
Bile acids, FGF15/19 and liver regeneration: From mechanisms to clinical applications.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018 Apr;1864(4 Pt B):1326-1334. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.06.025. Epub 2017 Jul 12. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018. PMID: 28709961 Review.
-
Bile acids: regulation of synthesis.J Lipid Res. 2009 Oct;50(10):1955-66. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R900010-JLR200. Epub 2009 Apr 3. J Lipid Res. 2009. PMID: 19346330 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Elevated Levels of Toxic Bile Acids in Serum of Cystic Fibrosis Patients with CFTR Mutations Causing Pancreatic Insufficiency.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 18;23(20):12436. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012436. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293293 Free PMC article.
-
Markers of liver regeneration-the role of growth factors and cytokines: a systematic review.BMC Surg. 2020 Feb 12;20(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s12893-019-0664-8. BMC Surg. 2020. PMID: 32050952 Free PMC article.
-
The integrated analysis of gut microbiota and metabolome revealed steroid hormone biosynthesis is a critical pathway in liver regeneration after 2/3 partial hepatectomy.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 12;15:1407401. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1407401. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39188944 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular pathways of liver regeneration: A comprehensive review.World J Hepatol. 2021 Mar 27;13(3):270-290. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i3.270. World J Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33815672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of cholestasis on portal vein embolization-induced hypertrophy of the future liver remnant.Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2023 Jan 21;408(1):54. doi: 10.1007/s00423-023-02784-w. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2023. PMID: 36680689 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoekstra LT, de Graaf W, Nibourg GA, Heger M, Bennink RJ, Stieger B, van Gulik TM. Physiological and biochemical basis of clinical liver function tests: A review. Ann Surg. 2013;257:27–36. - PubMed
-
- Michalopoulos GK. Advances in liver regeneration. Exp Rev Garstroenterol Hepatol. 2014;8:897–907. - PubMed
-
- Bismuth H, Majno PE. Hepatobiliary surgery. J Hepatol. 2000;32:208–224. - PubMed
-
- Togo S, Makino H, Kobayashi T, Morita T, Shimizu T, Kubota T, Ichikawa Y, Ishikawa T, Okazaki Y, Hayashizaki Y, Shimada H. Mechanism of liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy using mouse cdna microarray. J Hepatol. 2004;40:464–471. - PubMed
-
- Liao Y, Shikapwashya ON, Shteyer E, Dieckgraefe BK, Hruz PW, Rudnick DA. Delayed hepatocellular mitotic progression and impaired liver regeneration in early growth response-1-deficient mice. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:43107–43116. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
