Efficacy of Cilostazol Administration in Alzheimer's Disease Patients with White Matter Lesions: A Positron-Emission Tomography Study
- PMID: 30761509
- PMCID: PMC6554387
- DOI: 10.1007/s13311-018-00708-x
Efficacy of Cilostazol Administration in Alzheimer's Disease Patients with White Matter Lesions: A Positron-Emission Tomography Study
Abstract
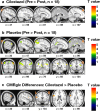
This study tested the efficacy of the phosphodiesterase type III inhibitor cilostazol in Alzheimer's disease patients with white matter lesions treated with donepezil in comparison with donepezil monotherapy using fluorodeoxyglucose (18F) positron-emission tomography (FDG PET). A 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study was conducted. Thirty-six Alzheimer's disease patients with white matter lesions who received donepezil (n = 18 each in the cilostazol and placebo groups) were enrolled. Participants underwent pre and post FDG PET imaging scans and three rounds of clinical and neuropsychological tests. The cilostazol group did not show a significant decrease of regional glucose metabolism; however, regional glucose metabolism was significantly decreased in the parietal and frontal lobes of the placebo group. The repeated measures ANOVA measuring differences in uptake change revealed that regional glucose metabolism in the left inferior frontal gyrus was significantly more preserved in the cilostazol group than that in the placebo group (p < 0.005). Mean changes from baseline on the Mini-Mental State Exam, Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale-cognitive subscale, Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study-Activities of Daily Living Inventory, and the Clinical Dementia Rating Sum of Boxes did not differ between the two groups. In the cilostazol group, the increase of glucose metabolism correlated with the improvment of the Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale-cognitive score. We conclude that cilostazol treatment added to donepezil may delay the decline in regional cerebral metabolism in Alzheimer's disease with white matter lesions compared with donepezil monotherapy. In additon, our results verified the efficacy of cilostazol in improving or protecting cognitive function in Alzheimer's disease through increased glucose metabolism. However, the long-term effect of cilostazol on cognitive function and Alzheimer's disease modification must be tested in further studies with larger sample size and longer study period. Trial registration: http://clinicaltrials.gov : NCT01409564.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; cilostazol; positron-emission tomography study.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Lee JH, Park SY, Shin YW, Hong KW, Kim CD, Sung SM, et al. Neuroprotection by cilostazol, a phosphodiesterase type 3 inhibitor, against apoptotic white matter changes in rat after chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Brain research. 2006;1082(1):182–91. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.01.088. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Patil CS, Singh VP, Kulkarni SK. Modulatory effect of sildenafil in diabetes and electroconvulsive shock-induced cognitive dysfunction in rats. Pharmacol Rep. 2006;58(3):373–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

