Superior efficacy of insulin degludec/liraglutide versus insulin glargine U100 as add-on to sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor therapy: A randomized clinical trial in people with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 30761720
- PMCID: PMC6593861
- DOI: 10.1111/dom.13666
Superior efficacy of insulin degludec/liraglutide versus insulin glargine U100 as add-on to sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor therapy: A randomized clinical trial in people with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the efficacy and safety of insulin degludec/liraglutide (IDegLira) versus insulin glargine 100 units/mL (IGlar U100) as add-on to sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor therapy.
Materials and methods: In this 26-week, phase IIIb, open-label, parallel-group, treat-to-target trial, conducted at 74 sites in 11 countries, insulin-naïve people aged ≥18 years with glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) 53-97 mmol/mol (7.0-11.0%), body mass index 20-40 kg/m2 and inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes (T2D) on SGLT2 inhibitor ± oral antidiabetic drugs were randomized 1:1 to once-daily IDegLira or IGlar U100, both as add-on to existing therapy. The primary endpoint was change in HbA1c from baseline to week 26.
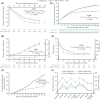
Results: A total of 210 participants were randomized to each treatment arm. Mean HbA1c reductions were 21 mmol/mol (1.9%-points) with IDegLira and 18 mmol/mol (1.7%-points) with IGlar U100; confirming non-inferiority (P < 0.0001) and superiority of IDegLira (difference in HbA1c change -3.90 mmol/mol; 95% confidence interval [CI] -5.45; -2.35 (-0.36%-points; 95% CI -0.50, -0.21)). Superiority for IDegLira over IGlar U100 was also confirmed for: body weight (difference -1.92 kg; 95% CI -2.64, -1.19); severe or blood-glucose-confirmed symptomatic hypoglycaemia (rate ratio 0.42; 95% CI 0.23, 0.75); total daily insulin dose (difference -15.37 U; 95% CI -19.60, -11.13). The overall treatment-emergent adverse event rate was higher with IDegLira as a result of higher increased lipase and nausea rates.
Conclusions: The favourable safety and efficacy profile of IDegLira in people with uncontrolled T2D on SGLT2 inhibitors, and lower weight gain and hypoglycaemia risk versus IGlar U100, suggest that clinicians should consider IDegLira initiation in this population.
Keywords: GLP-1 analogue; SGLT2 inhibitor; insulin therapy; liraglutide; randomized trial; type 2 diabetes.
© 2019 The Authors. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
A.P.‐T. reports advisor and educational grants with no direct or indirect reimbursement to advisor from Sanofi; advisor and research supplies with no direct or indirect reimbursement to advisor from Dexcom, advisor and educational grants with no direct or indirect reimbursement to advisor from Lilly, advisor and educational grants with no direct or indirect reimbursement to advisor from Novo Nordisk, and being a stockholder of Ionis, during the conduct of the study. L.K.B. reports personal fees from Novo Nordisk, personal fees from Sanofi and personal fees from Dexcom, outside the submitted work. R.B. reports personal fees from Novo Nordisk, grants from Novo Nordisk, grants from Sanofi, grants from AstraZeneca, grants from Lilly, grants from Lexicon Pharmaceuticals and grants from Bayer during the conduct of the study. C.M.P. reports no relevant conflicts of interest. R.S. reports personal fees from Novo Nordisk, personal fees from Sanofi, personal fees from Eli Lilly, personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and personal fees from AstraZeneca, outside the submitted work. N.H. is an employee of Novo Nordisk. S.E. is an employee of Novo Nordisk. K.B. reports employment by Novo Nordisk. S.H. reports financial relationships with Sanofi, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Janssen, Merck, AstraZeneca, Abbott, Boehringer Ingelheim, JDRF, Lawson, Medtronic, Amgen and Health Canada/First Nations and Inuit Health Branch.
Figures

References
-
- American Diabetes Association . 8. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of medical care in diabetes 2018. Diabetes Care. 2018;41:S73‐S85. - PubMed
-
- Gough SC, Bode B, Woo V, et al. Efficacy and safety of a fixed‐ratio combination of insulin degludec and liraglutide (IDegLira) compared with its components given alone: results of a phase 3, open‐label, randomised, 26‐week, treat‐to‐target trial in insulin‐naive patients with type 2 diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014;2:885‐893. - PubMed
-
- Buse JB, Vilsbøll T, Thurman J, et al. Contribution of liraglutide in the fixed‐ratio combination of insulin degludec and liraglutide (IDegLira). Diabetes Care. 2014;37:2926‐2933. - PubMed
-
- Lingvay I, Pérez Manghi F, Garcia‐Hernandez P, et al. Effect of insulin glargine up‐titration vs insulin degludec/liraglutide on glycated hemoglobin levels in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes: The DUAL V randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016;315:898‐907. - PubMed

