Inhibition of α5 GABAA receptors has preventive but not therapeutic effects on isoflurane-induced memory impairment in aged rats
- PMID: 30762015
- PMCID: PMC6404482
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.250621
Inhibition of α5 GABAA receptors has preventive but not therapeutic effects on isoflurane-induced memory impairment in aged rats
Abstract
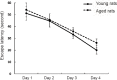
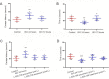
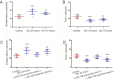
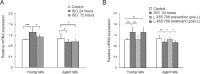
The α5 subunit-containing gamma-amino butyric acid type A receptors (α5 GABAARs) are a distinct subpopulation that are specifically distributed in the mammalian hippocampus and also mediate tonic inhibitory currents in hippocampal neurons. These tonic currents can be enhanced by low-dose isoflurane, which is associated with learning and memory impairment. Inverse agonists of α5 GABAARs, such as L-655,708, are able to reverse the short-term memory deficit caused by low-dose isoflurane in young animals. However, whether these negative allosteric modulators have the same effects on aged rats remains unclear. In the present study, we mainly investigated the effects of L-655,708 on low-dose (1.3%) isoflurane-induced learning and memory impairment in elderly rats. Young (3-month-old) and aged (24-month-old) Wistar rats were randomly assigned to receive L-655,708 0.5 hour before or 23.5 hours after 1.3% isoflurane anesthesia. The Morris Water Maze tests demonstrated that L-655,708 injected before or after anesthesia could reverse the memory deficit in young rats. But in aged rats, application of L-655,708 only before anesthesia showed similar effects. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction showed that low-dose isoflurane decreased the mRNA expression of α5 GABAARs in aging hippocampal neurons but increased that in young animals. These findings indicate that L-655,708 prevented but could not reverse 1.3% isoflurane-induced spatial learning and memory impairment in aged Wistar rats. All experimental procedures and protocols were approved by the Experimental Animal Ethics Committee of Academy of Military Medical Science of China (approval No. NBCDSER-IACUC-2015128) in December 2015.
Keywords: M2 type microglia; Wnt/Frizzled signaling pathway; early brain injury; inflammatory cytokines; nerve regeneration; neural regeneration; nuclear factor-κB; peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ; subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neuroprotection mediated by the Wnt/Frizzled signaling pathway in early brain injury induced by subarachnoid hemorrhage.Neural Regen Res. 2019 Jun;14(6):1013-1024. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.250620. Neural Regen Res. 2019. PMID: 30762013 Free PMC article.
-
Selective inhibition of extra-synaptic α5-GABAA receptors by S44819, a new therapeutic agent.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Oct;125:353-364. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.08.012. Epub 2017 Aug 12. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28807671
-
Short-term memory impairment after isoflurane in mice is prevented by the α5 γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor inverse agonist L-655,708.Anesthesiology. 2010 Nov;113(5):1061-71. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181f56228. Anesthesiology. 2010. PMID: 20966663
-
GABAA receptor subtype-selective modulators. II. α5-selective inverse agonists for cognition enhancement.Curr Top Med Chem. 2011;11(9):1203-14. doi: 10.2174/156802611795371314. Curr Top Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21050171 Review.
-
The α5-Containing GABAA Receptors-a Brief Summary.J Mol Neurosci. 2019 Feb;67(2):343-351. doi: 10.1007/s12031-018-1246-4. Epub 2019 Jan 3. J Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30607899 Review.
Cited by
-
GLYX-13 pretreatment ameliorates long-term isoflurane exposure-induced cognitive impairment in mice.Neural Regen Res. 2020 Jan;15(1):128-135. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.264466. Neural Regen Res. 2020. PMID: 31535661 Free PMC article.
-
Neurobiology and Therapeutic Potential of α5-GABA Type A Receptors.Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 Jul 24;12:179. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00179. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31396049 Free PMC article.
-
Sevoflurane-induced overexpression of extrasynaptic α5-GABAAR via the RhoA/ROCK2 pathway impairs cognitive function in aged mice.Aging Cell. 2024 Sep;23(9):e14209. doi: 10.1111/acel.14209. Epub 2024 Jun 2. Aging Cell. 2024. PMID: 38825816 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term α5 GABA A receptor negative allosteric modulator treatment reduces NMDAR-mediated neuronal excitation and maintains basal neuronal inhibition.Neuropharmacology. 2023 Oct 1;237:109587. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2023.109587. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Neuropharmacology. 2023. PMID: 37270156 Free PMC article.
-
A multi-dosing regimen to enhance the spatial memory of normal rats with α5-containing GABAA receptor negative allosteric modulator L-655,708.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021 Dec;238(12):3375-3389. doi: 10.1007/s00213-021-05951-3. Epub 2021 Aug 14. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021. PMID: 34389882
References
-
- Atack JR. Preclinical and clinical pharmacology of the GABA A, receptor α5 subtype-selective inverse agonist α5IA. Pharmacol Ther. 2010;125:11–26. - PubMed
-
- Callaway JK, Jones NC, Royse AG, Royse CF. Memory impairment in rats after desflurane anesthesia is age and dose dependent. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;44:995–1005. - PubMed
-
- Caraiscos VB, Elliott EM, You-Ten KE, Cheng VY, Belelli D, Newell JG, Jackson MF, Lambert JJ, Rosahl TW, Wafford KA, MacDonald JF, Orser BA. Tonic inhibition in mouse hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons is mediated by α5 subunit-containing γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004b;101:3662–3667. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

