Nuclear pore protein TPR associates with lamin B1 and affects nuclear lamina organization and nuclear pore distribution
- PMID: 30762072
- PMCID: PMC11105453
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-019-03037-0
Nuclear pore protein TPR associates with lamin B1 and affects nuclear lamina organization and nuclear pore distribution
Abstract
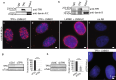
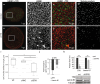
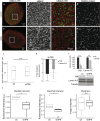
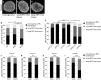
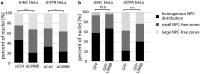
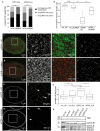
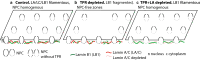
The organization of the nuclear periphery is crucial for many nuclear functions. Nuclear lamins form dense network at the nuclear periphery and play a substantial role in chromatin organization, transcription regulation and in organization of nuclear pore complexes (NPCs). Here, we show that TPR, the protein located preferentially within the nuclear baskets of NPCs, associates with lamin B1. The depletion of TPR affects the organization of lamin B1 but not lamin A/C within the nuclear lamina as shown by stimulated emission depletion microscopy. Finally, reduction of TPR affects the distribution of NPCs within the nuclear envelope and the effect can be reversed by simultaneous knock-down of lamin A/C or the overexpression of lamin B1. Our work suggests a novel role for the TPR at the nuclear periphery: the TPR contributes to the organization of the nuclear lamina and in cooperation with lamins guards the interphase assembly of nuclear pore complexes.
Keywords: Image analysis; Lamina; Lamins; Nuclear pore complex; Nucleus; Super-resolution imaging; TPR; Translocated promoter region.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Schermelleh L, Carlton PM, Haase S, Shao L, Winoto L, Kner P, Burke B, Cardoso MC, Agard DA, Gustafsson MG, Leonhardt H, Sedat JW. Subdiffraction multicolor imaging of the nuclear periphery with 3D structured illumination microscopy. Science. 2008;320(5881):1332–1336. doi: 10.1126/science.1156947. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

