Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Models for CYP1A2 Drug-Drug Interaction Prediction: A Modeling Network of Fluvoxamine, Theophylline, Caffeine, Rifampicin, and Midazolam
- PMID: 30762305
- PMCID: PMC6539736
- DOI: 10.1002/psp4.12397
Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Models for CYP1A2 Drug-Drug Interaction Prediction: A Modeling Network of Fluvoxamine, Theophylline, Caffeine, Rifampicin, and Midazolam
Abstract
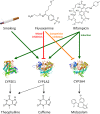
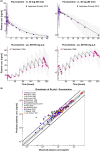
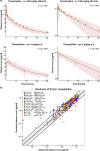
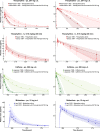
This study provides whole-body physiologically-based pharmacokinetic models of the strong index cytochrome P450 (CYP)1A2 inhibitor and moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor fluvoxamine and of the sensitive CYP1A2 substrate theophylline. Both models were built and thoroughly evaluated for their application in drug-drug interaction (DDI) prediction in a network of perpetrator and victim drugs, combining them with previously developed models of caffeine (sensitive index CYP1A2 substrate), rifampicin (moderate CYP1A2 inducer), and midazolam (sensitive index CYP3A4 substrate). Simulation of all reported clinical DDI studies for combinations of these five drugs shows that the presented models reliably predict the observed drug concentrations, resulting in seven of eight of the predicted DDI area under the plasma curve (AUC) ratios (AUC during DDI/AUC control) and seven of seven of the predicted DDI peak plasma concentration (Cmax ) ratios (Cmax during DDI/Cmax control) within twofold of the observed values. Therefore, the models are considered qualified for DDI prediction. All models are comprehensively documented and publicly available, as tools to support the drug development and clinical research community.
© 2019 The Authors CPT: Pharmacometrics & Systems Pharmacology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
T.E., T.W., and S.F. are employees of Bayer AG. A.K.V. performed this work at the Saarland University. Since January 2018, she is an employee of the Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices (BfArM) and declares no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the other authors.
Figures

References
-
- Shimada, T. , Yamazaki, H. , Mimura, M. , Inui, Y. & Guengerich, F.P. Interindividual variations in human liver cytochrome P‐450 enzymes involved in the oxidation of drugs, carcinogens and toxic chemicals: studies with liver microsomes of 30 Japanese and 30 caucasians. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 270, 414–423 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Kalow, W. & Tang, B. The use of caffeine for enzyme assays: a critical appraisal. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 53, 503–514 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Karjalainen, M.J. , Neuvonen, P.J. & Backman, J.T. Rofecoxib is a potent, metabolism‐dependent inhibitor of CYP1A2: implications for in vitro prediction of drug interactions. Drug Metab. Dispos. 34, 2091–2096 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

