Effectiveness and safety of fluoxetine for premature ejaculation: Protocol for a systematic review
- PMID: 30762772
- PMCID: PMC6407935
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014481
Effectiveness and safety of fluoxetine for premature ejaculation: Protocol for a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Premature ejaculation (PE) is one of the most common male sexual dysfunctions, which can directly harm men's self-esteem and affect the stability of the relationship between husband and wife. To some extent, PE even affects the harmony and stability of society. So, men's health has gained more and more attention. As one of the long-acting selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), fluoxetine has been proven to be effective in the treatment of PE by many trails. In this study, we aim to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of fluoxetine for PE to provide the newest evidence for clinical use.
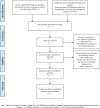
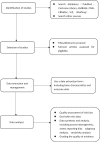
Methods and analysis: Literature research will be divided into 2 parts: electronic search and manual search. We will search PubMed, EMBASE, The Cochrane Library, the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), China Biology Medicine disc (CBMdisc), the China Science and Technology Journal database (VIP), and the Wanfang database online. We will select the eligible studies published up to December 31, 2018. Manual searches mainly retrieve dissertations, ongoing trails, internal reports, and so on. We use intravaginal ejaculatory latency time (IELT) as the primary outcome of PE and we also care about the following indexes: PE Diagnostic Tool (PEDT); Arabic index of PE (AIPE); Index of PE (IPE). In addition, we will carefully observe the patient's adverse reactions during the medication. Two reviewers will read the articles, extract the data information, and assess the risk of bias independently. Data analysis will be used the software such as RevMan V.5.3.5; EndNote X7 and Stata 13.0.
Results: This study will provide a high-quality synthesis of current evidence of fluoxetine for PE from several aspects, including IELT, PEDT, AIPE, IPE, and adverse events.
Conclusion: This systematic review will provide evidence to assess the effectiveness and safety of fluoxetine in the treatment of PE.
Trial registration number: PROSPERO CRD42018109722.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Gao J, Zhang X, Su P, et al. Prevalence and factors associated with the complaint of premature ejaculation and the four premature ejaculation syndromes: a large observational study in China. J Sex Med 2013;10:1874–81. - PubMed
-
- Porst H, Montorsi F, Rosen RC, et al. The Premature Ejaculation Prevalence and Attitudes (PEPA) survey: prevalence, comorbidities, and professional help-seeking. Eur Urol 2007;51:816–23. discussion 24. - PubMed
-
- Son H, Song SH, Lee JY, et al. Relationship between premature ejaculation and depression in Korean males. J Sex Med 2011;8:2062–70. - PubMed
-
- Serefoglu EC, Yaman O, Cayan S, et al. Prevalence of the complaint of ejaculating prematurely and the four premature ejaculation syndromes: results from the Turkish Society of Andrology Sexual Health Survey. J Sex Med 2011;8:540–8. - PubMed
-
- Waldinger MD, Quinn P, Dilleen M, et al. A multinational population survey of intravaginal ejaculation latency time. J Sex Med 2005;2:492–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials