The effectiveness and safety of cervus and cucumis polypeptide injection in promoting fracture healing after bone fracture surgeries: Protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 30762805
- PMCID: PMC6408092
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014571
The effectiveness and safety of cervus and cucumis polypeptide injection in promoting fracture healing after bone fracture surgeries: Protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Bone fractures are a common occurrence, and, according to clinical investigations, approximately 5% to 10% of patients with fractures will suffer from delayed healing or even non-healing. The high efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine in promoting fracture healing has been fully verified over a long history of diagnosis and treatment. Traditional Chinese medicine has a long history of applying Chinese herbs to treat fractures. Cervus and cucumis polypeptide injection has been widely used to promote fracture healing after fracture surgery in clinic, but its efficacy and safety are controversial. For the above reasons, the purpose of this study is to systematically evaluate the efficacy and safety of cervus and cucumis polypeptide injection in promoting fracture healing after bone fracture surgeries and to provide a theoretical basis for the selection of appropriate treatment measures for delayed healing of patients with fractures.
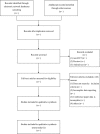
Methods: A total of 8 databases were searched, including the non-Chinese-language databases PubMed, The Cochrane Library, Web of Science, and Embase and the Chinese databases Chongqing VIP Chinese Journal Service Platform (VIP), Wanfang Data Knowledge Service Platform (Wanfang Data), SinoMed and Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI). The databases were queried for publicly released randomized controlled trials of the effectiveness and safety of Cervus and Cucumis polypeptide injection for fracture healing after surgical treatment, and no language restrictions were imposed. The software Review Manager 5.3 was used to evaluate the quality of the selected documents, and Stata 12.0 software was used for statistical analysis.
Results: This review will be to assess the efficacy and safety of cervus and cucumis polypeptide injection in promoting fracture healing after bone fracture surgeries.
Conclusion: Our study will use systematic evaluation to objectively evaluate the efficacy and safety of cervus and cucumis polypeptide injection in promoting fracture healing after fracture surgery. It will provide theoretical basis for guiding clinical practice and benefit more patients.
Ethics and dissemination: This study is a systematic review that does not require ethical approval and meets the requirements of protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. At the same time, this study does not involve the recruitment of patients. All data are from published academic papers.
Protocol and registration: A protocol had been registered for this systematic review and meta-analysis in PROSPERO. (registration number: CRD42019120965).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Clinical analysis of Cervus and Cucumis Polypeptide injection based on real world hospital information system].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016 Nov;41(21):4060-4065. doi: 10.4268/cjcmm20162127. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 28929696 Chinese.
-
The study on the clinical effectiveness and safety of traditional Chinese medicine acupoint catgut embedding guided by musculoskeletal ultrasound in the treatment of nerve root sciatica: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Apr 2;100(13):e25387. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025387. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33787646 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of Chinese medicines for vitreous hemorrhage: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 May;99(19):e20086. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000020086. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32384479 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of bone morphogenetic protein and autologous grafting in the treatment of limb long bone nonunion: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2020 Jul 29;15(1):288. doi: 10.1186/s13018-020-01805-4. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020. Retraction in: J Orthop Surg Res. 2021 May 29;16(1):345. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02491-6. PMID: 32727538 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Efficacy and safety of traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of epilepsy by wind quenching and phlegm resolving: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Oct 25;103(43):e39942. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039942. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39470546 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cervus and cucumis peptides combined umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells therapy for rheumatoid arthritis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Jul 10;99(28):e21222. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000021222. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32664175 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Xiao W, Yang X, Wang Y, et al. Splenectomy delays fracture healing by affecting the level of tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 6 and bone morphogenetic protein. Adv Clin Exp Med 2018;27:165–71. - PubMed
-
- Zhao C, Zhang BZ, Feng HL. Mechanism and experimental research progress of traditional Chinese medicine on the intervention of fracture healing. Hebei J Tradit Chin Med 2017;39:1904–7.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical