IL-1 inhibition improves insulin resistance and adipokines in rheumatoid arthritis patients with comorbid type 2 diabetes: An observational study
- PMID: 30762811
- PMCID: PMC6408058
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014587
IL-1 inhibition improves insulin resistance and adipokines in rheumatoid arthritis patients with comorbid type 2 diabetes: An observational study
Abstract
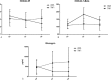
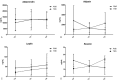
Recently, it has been shown that some well-known pathogenic mediators in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF), could play a pathogenic role in insulin resistance and (IR) and type 2 diabetes (T2D).In this 6-month longitudinal study, we aimed at investigating if the inhibition of IL-1 or TNF is associated with an improvement of IR in RA patients with comorbid T2D and the possible effects on selected serum adipokines. RA patients with comorbid T2D were recruited among those undergoing treatment with anakinra (ANA) or with TNF inhibitor (TNFi). The 1998-updated version of the Homeostasis Model Assessment (HOMA2) was used to calculate surrogate indexes of IR (HOMA2-IR) and steady-state beta cell function (%B) from fasting values of glucose and C-peptide. Glucagon, adiponectin, adipsin, leptin, and resistin were also measured. All these parameters were collected at baseline, after 3 and 6 months of treatment.ANA-treated patients showed a significant improvement in HOMA2-%β, HOMA2-IR, and glucagon. In TNFi-treated patients, no significant difference was observed analyzing these metabolic parameters. Adipsin and resistin decreased after 6 months in ANA-treated patients whereas, no difference was recognized analyzing adiponectin and leptin. In TNFi-treated patients, leptin and resistin significantly increased, whereas no difference was found analyzing adiponectin and adipsin, during the follow-up.Our data may suggest a beneficial effect of IL-1 inhibition on measures of metabolic derangement in RA-associated T2D. If further confirmed by larger studies, IL-1 targeting therapies may represent a tailored approach in these patients.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors have disclosed no conflict of interest for this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-interleukin-1 treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and type 2 diabetes (TRACK): A multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial.PLoS Med. 2019 Sep 12;16(9):e1002901. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002901. eCollection 2019 Sep. PLoS Med. 2019. PMID: 31513665 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Changes in serum adipokines profile and insulin resistance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-TNF-α.Curr Med Res Opin. 2019 Dec;35(12):2197-2205. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2019.1654988. Epub 2019 Sep 13. Curr Med Res Opin. 2019. PMID: 31397188
-
The effects of suppressing inflammation by tofacitinib may simultaneously improve glycaemic parameters and inflammatory markers in rheumatoid arthritis patients with comorbid type 2 diabetes: a proof-of-concept, open, prospective, clinical study.Arthritis Res Ther. 2024 Jan 4;26(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03249-7. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38178250 Free PMC article.
-
Adipokines and hepatic insulin resistance.J Diabetes Res. 2013;2013:170532. doi: 10.1155/2013/170532. Epub 2013 May 16. J Diabetes Res. 2013. PMID: 23762871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the Relationship between Adipokines and β-cell Failure in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2016 Oct 10;38(5):601-606. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2016.05.020. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2016. PMID: 27825421 Review.
Cited by
-
The effects of mindfulness-based stress reduction therapy combined with intensive education on the effectiveness of the care and the awareness rate in patients with arthritis and diabetes.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Apr 15;13(4):3190-3197. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34017488 Free PMC article.
-
Fasting triglycerides and glucose index: a useful screening test for assessing insulin resistance in patients diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2019 Nov 27;11:95. doi: 10.1186/s13098-019-0495-x. eCollection 2019. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2019. PMID: 31788032 Free PMC article.
-
Immediate-release tofacitinib reduces insulin resistance in non-diabetic active rheumatoid arthritis patients: A single-center retrospective study.World J Diabetes. 2022 Jun 15;13(6):454-465. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i6.454. World J Diabetes. 2022. PMID: 35800413 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation in obesity, diabetes, and related disorders.Immunity. 2022 Jan 11;55(1):31-55. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.12.013. Immunity. 2022. PMID: 35021057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary Quality Associated with Self-Reported Diabetes, Osteoarthritis, and Rheumatoid Arthritis among Younger and Older US Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study Using NHANES 2011-2016.Nutrients. 2021 Feb 7;13(2):545. doi: 10.3390/nu13020545. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33562353 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barile A, Arrigoni F, Bruno F, et al. Computed tomography and MR imaging in rheumatoid arthritis. Radiol Clin North Am 2017;55:997–1007. - PubMed
-
- Giacomelli R, Gorla R, Trotta F, et al. Quality of life and unmet needs in patients with inflammatory arthropathies: results from the multicentre, observational RAPSODIA study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2015;54:792–7. - PubMed
-
- Ruscitti P, Margiotta DPE, Macaluso F, et al. Subclinical atherosclerosis and history of cardiovascular events in Italian patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results from a cross-sectional, multicenter GIRRCS (Gruppo Italiano di Ricerca in Reumatologia Clinica e Sperimentale) study. Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96:e8180. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cipriani P, Ruscitti P, Carubbi F, et al. Methotrexate: an old new drug in autoimmune disease. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 2014;10:1519–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

