Trend and projection of mortality rate due to non-communicable diseases in Iran: A modeling study
- PMID: 30763320
- PMCID: PMC6375574
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0211622
Trend and projection of mortality rate due to non-communicable diseases in Iran: A modeling study
Abstract
Background: Following the epidemiologic and demographic transition, non-communicable disease mortality is the leading cause of death in Iran. Projecting mortality trend can provide valuable tools for policy makers and planners. In this article, we have estimated the trend of non-communicable disease mortality during 2001-2015 and have projected it until 2030 at national and subnational levels in Iran.
Methods: The data employed was gathered from the Iranian death registration system and using the Spatio-temporal model, the trends of 4 major categories of non-communicable diseases (cancers, cardiovascular diseases, asthma and COPD, and diabetes) by 2030 were projected at the national and subnational levels.
Results: The results indicated that age standardized mortality rate for cancers, CVDs, and Asthma and COPD will continue to decrease in both sexes (cancers: from 81.8 in 2015 to 45.2 in 2030, CVDs: 307.3 to 173.0, and Asthma and COPD: from 52.1 to 46.6); however, in terms of diabetes, there is a steady trend in both sexes at national level (from 16.6 to 16.5). Age standardized mortality rates for cancers and CVDs, in males and females, were high in all provinces in 2001. The variation between the provinces is clearer in 2015, and it is expected to significantly decrease in all provinces by 2030.
Conclusion: Generally, the age standardized mortality rate from NCDs will decrease by 2030. Of course, given the experience of the past two decades in Iran, believing that the mortality rate will decrease may not be an easy notion to understand. However hard to believe, this decrease may be the result of better management of risk factors and early detection of patients due to more comprehensive care in all segments of society, as well as improved literacy and awareness across the country.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

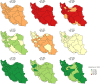
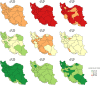
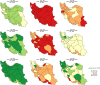


References
-
- The United Nations. Sustainable Development Goals. [cited 2018 1/10]; Available from: http://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/health/.
-
- (IHME)., I.f.H.M.a.E., et al. 2015 [cited 2018 1/10]; Available from: http://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-compare.
-
- Abegunde D.O., et al. , The burden and costs of chronic diseases in low-income and middle-income countries. The Lancet, 2007. 370(9603): p. 1929–1938. - PubMed
-
- Kontis V., et al. , Contribution of six risk factors to achieving the 25×25 non-communicable disease mortality reduction target: a modelling study. The Lancet, 2014. 384(9941): p. 427–437. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

